【VUE3+AntV X6】 引入ANTV X6 的流程图编辑器应用(一)
ANTV X6 流程图编辑器应用
- 唠唠叨叨
- 事发背景
- 实现效果
- 实现思路
- 总结
- 参考资���
唠唠叨叨
唉!最近感觉非常忙,要学的东西太多,要实现的方法变幻莫测,层出不穷,越学越觉得自己不会的实在太多。 项目本来中标了,后来又不知道发生了什么,临到签合同又黄了,整的我们开发的瑟瑟发抖,产品整个大改,恐怕要…… 只能说还是抓紧时间好好学习,知识和技术是永远不会背叛自己的。
事发背景
俺滴组长(后端大佬)要我配合开发数据平台的任务流全局调度系统,想用流程图实现作业运行配置。 于是我在各种流程图的前端框架中选了ANTV X6来引入实现。官方文档天天在看,可这知识他就是不入脑子呀TvT。 终于有一天腌肉某人一拍脑门醍醐灌顶实现了功能,遂记录实现过程及困难解决方法。
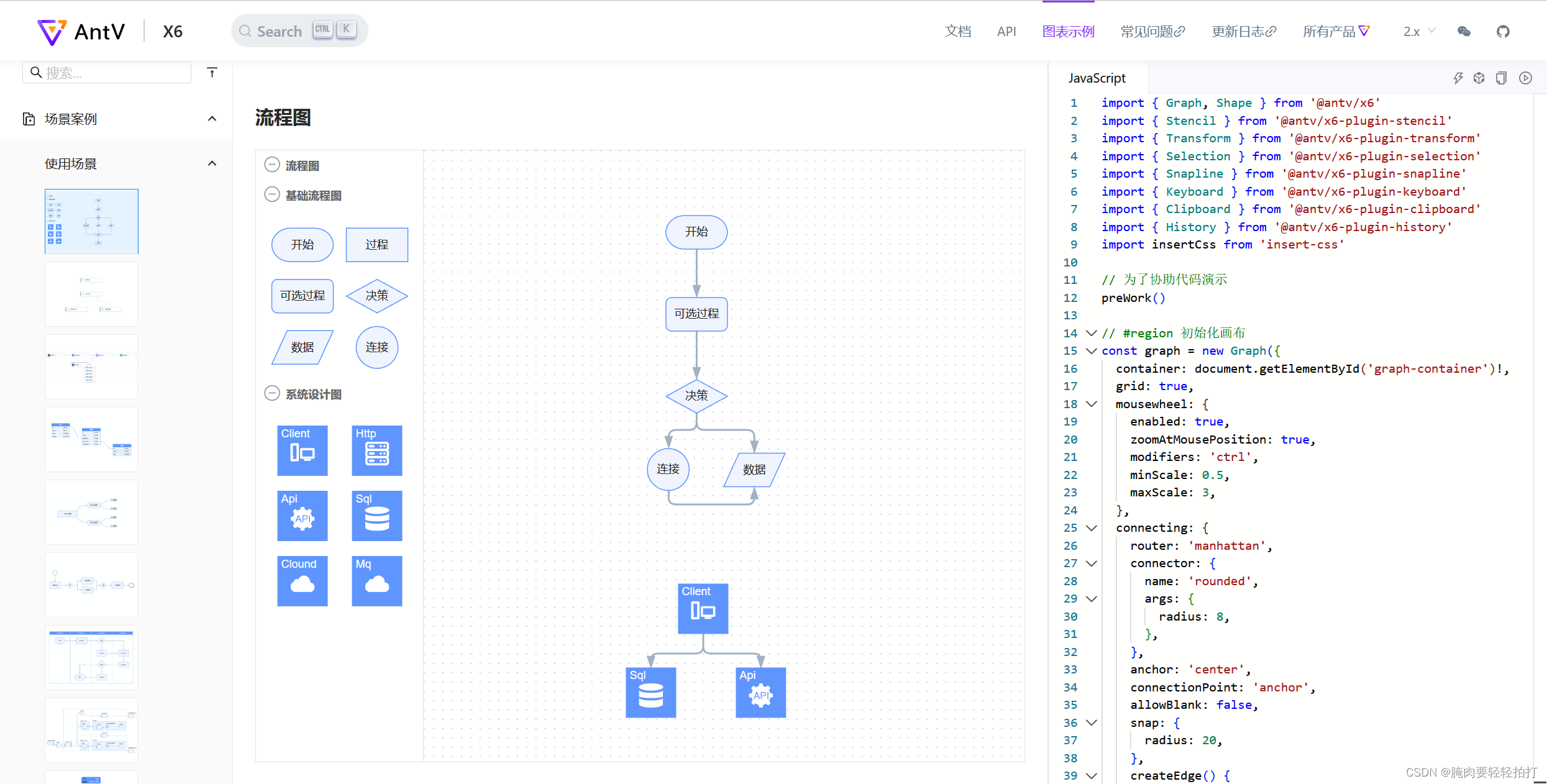
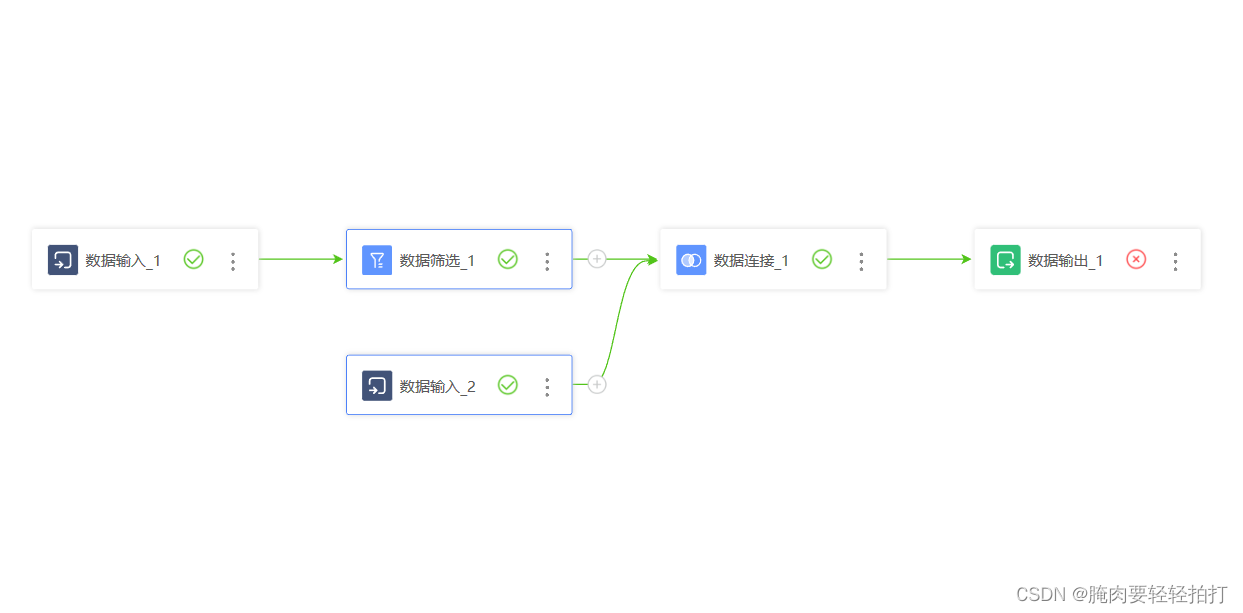
在官方文档中给出了场景案例,恰好就有我所需要的流程图:
实现效果
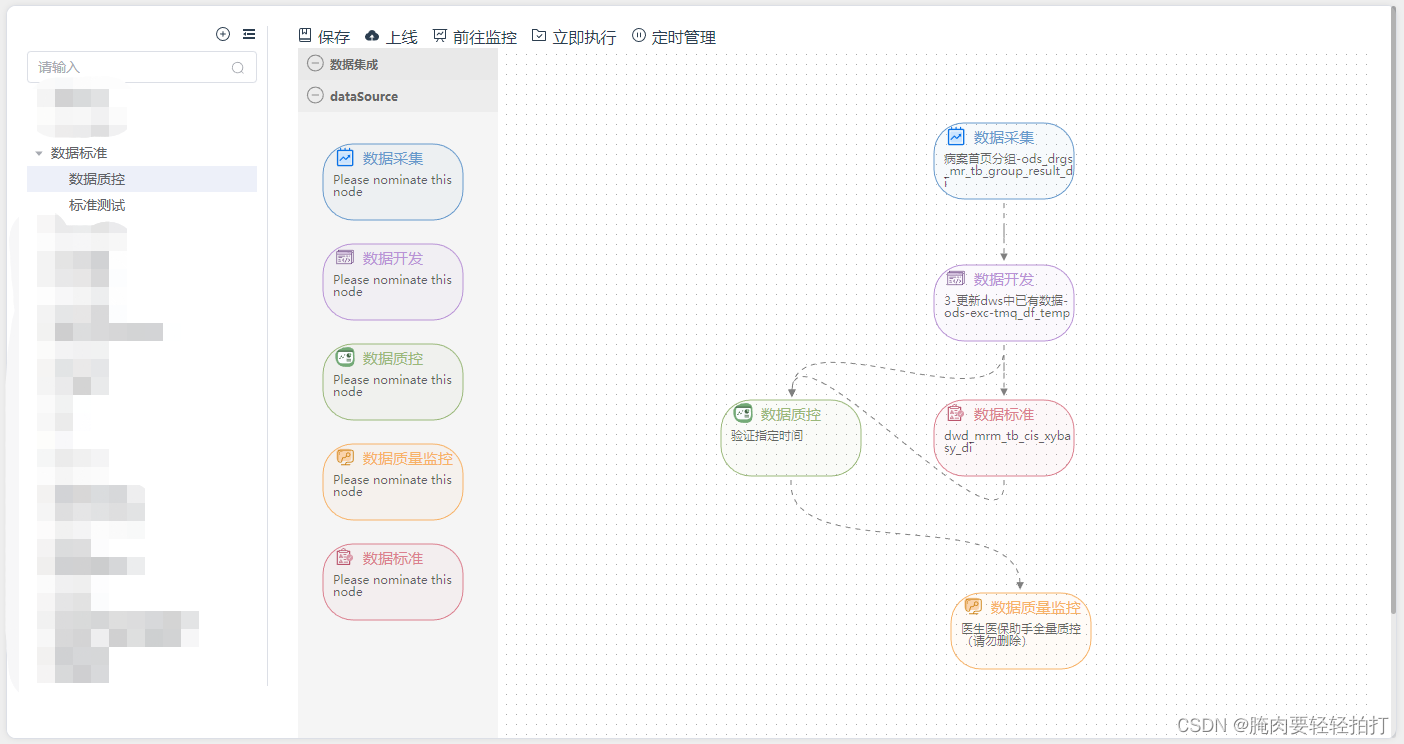
经过一系列拼拼凑凑,修修改改,还有样式设计和调整,调度作业画布页面如下图所示:
实现思路
- 首先我们要了解系统的业务功能需求,以及业务流程的线路是怎样的;
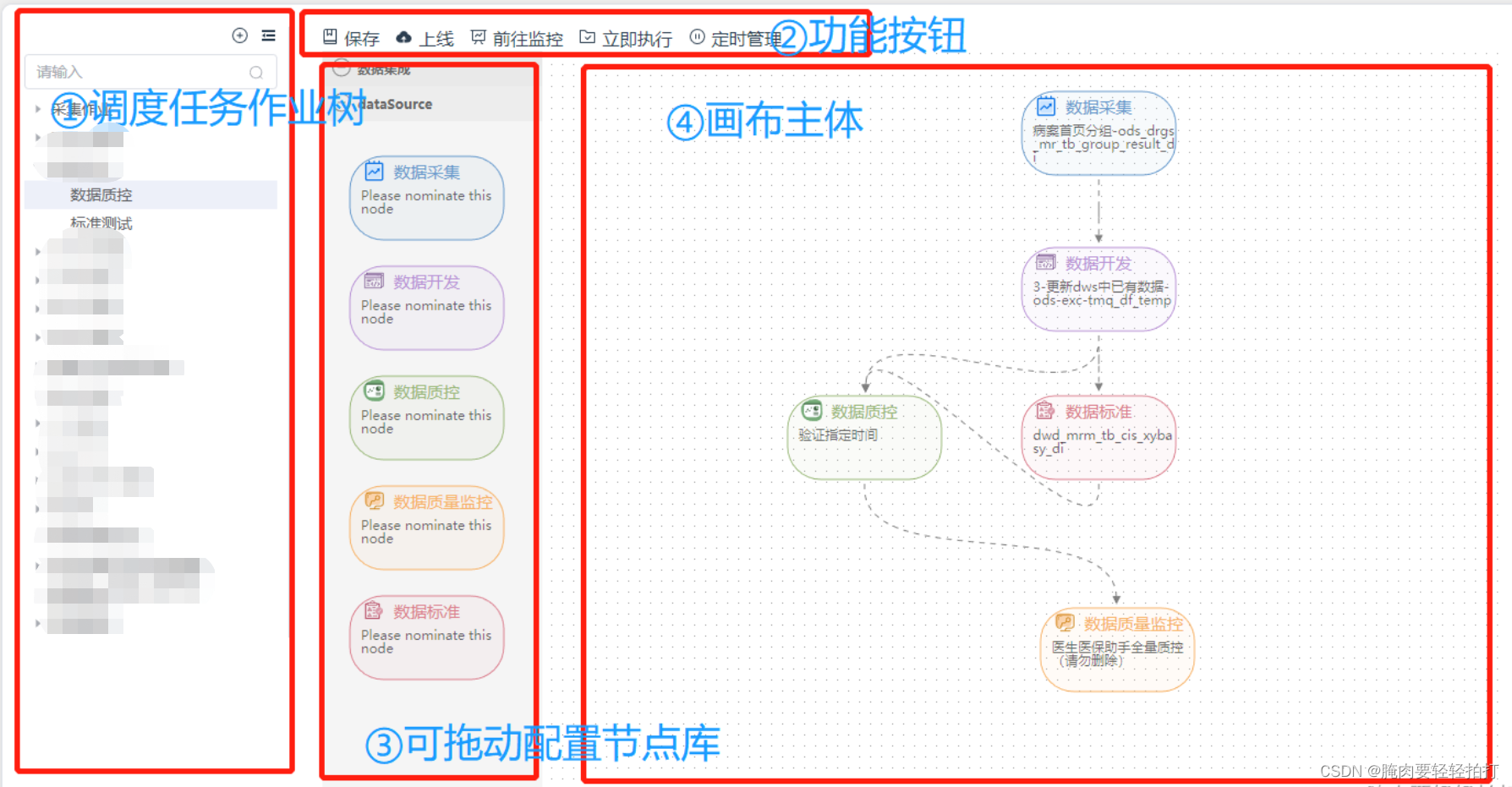
如图是窗口的拆解,其中①作业树使用的是element UI的el-tree组件,是用于储存画布内容和画布回显更新的,②是选中节点树中的某项流程作业进行对应的任务操作,③和④才是实际应用AntV X6的画布插件实现的可拖拽、增、删、改、配置的流程图编辑器。
通过vue的父子组件我们创建一个index.vue的父组件,然后将这四个部分拆分为三个子组件的.vue文件,分别为DataTree.vue、DataButton.vue、FiliationGraph.vue(包含③、④两部分)今天记录的是FiliationGraph.vue内节点配置画布的实现。
2. 安装AntV X6
通过 npm 或 yarn 命令安装 X6。
# npm $ npm install @antv/x6 --save # yarn $ yarn add @antv/x6
- 初始化画布,在html中建立节点库和画布div容器:
// 引入 import { Graph, Shape, Addon, FunctionExt } from "@antv/x6"; const { Stencil } = Addon; //节点库 const {graph} = Graph; //画布 const stencil = new Stencil({ //新建节点库 title: "数据集成", target: graph, search: false, // 搜索 collapsable: true, stencilGraphWidth: 300, //容器宽度 stencilGraphHeight: 600, //容器长度 groups: [ //分组 { name: "processLibrary", title: "dataSource", }, ], layoutOptions: { dx: 30, dy: 20, columns: 1, //列数(行内节点数) columnWidth: 130, //列宽 rowHeight: 100, //行高 }, }); proxy.$refs.stencilContainer.appendChild(stencil.container) //注册到div中 const graph = new Graph({ // 新建画布 container: document.getElementById('flowContainer'), width: 800, height: 600, background: { color: "#F2F7FA", }, });- 初始化节点、边:
初始化节点、边数据:
const nodeData = { // 节点 nodes: [ ], // 边 edges: [ ], };准备节点样式内容数据,其中节点的左上角图标image是自定义的svg文件,根据产品ui或自己设计来使用哟。
const imageShapes = [ { body: { fill: "rgba(102, 153, 204, 0.05)", stroke: "rgb(102, 153, 204)", }, label: { text: state.collectLabel, fill: 'rgb(102, 153, 204)', }, image: require('/src/assets/Scheduler/DataCollect.svg'), }, { body: { fill: "rgba(185, 147, 214, 0.05)", stroke: "rgb(185, 147, 214)", }, label: { text: state.flinkLabel, fill: 'rgb(185, 147, 214)', }, image: require('/src/assets/Scheduler/DataFlink.svg'), }, { body: { fill: "rgba(154, 184, 122, 0.05)", stroke: "rgb(154, 184, 122)", }, label: { text: state.controlLabel, fill: 'rgb(154, 184, 122)', }, image: require('/src/assets/Scheduler/DataQc.svg'), }, { body: { fill: "rgba(247, 178, 103, 0.05)", stroke: "rgb(247, 178, 103)", }, label: { text: state.monitorLabel, fill: 'rgb(247, 178, 103)', }, image: require('/src/assets/Scheduler/DataWatch.svg'), }, { body: { fill: "rgba(219, 127, 142, 0.05)", stroke: "rgb(219, 127, 142)", }, label: { text: state.standerLabel, fill: 'rgb(219, 127, 142)', }, image: require('/src/assets/Scheduler/DataStandred.svg'), }, ]- 左侧模型栏节点样式:
初始化链接桩
const ports = { groups: { in: { position: 'top', attrs: { circle: { r: 4, magnet: true, stroke: '#108ee9', strokeWidth: 2, fill: '#fff', style: { visibility: "hidden", }, } } }, out: { position: 'bottom', attrs: { circle: { r: 4, magnet: true, stroke: '#31d0c6', strokeWidth: 2, fill: '#fff', style: { visibility: "hidden", }, } } } }, items: [ { id: state.currentCode+ '_in', group: 'in', }, { id: state.currentCode + '_out', group: 'out', }, ], }根据样式数据,设计画布左侧节点样式
Graph.registerNode( //注册节点 'custom-node', { inherit: 'rect', //基础图形 width: 140, height: 76, attrs: { //自定义样式 body: { //节点主体 strokeWidth: 1, rx: 30, ry: 30, }, image: { //图片 width: 20, height: 20, x: 12, y: 3, }, text: { //主题文本 refX: 40, refY: 15, fontSize: 15, 'text-anchor': 'start', }, label: { //标签名 text: 'Please nominate this node', id: 0, //自定义传给接口的数据 data: {}, //这里是我加入的标签内自定义储存的数据内容 refX: 10, refY: 30, fontSize: 12, fill: 'rgba(0,0,0,0.6)', 'text-anchor': 'start', textWrap: { //如果节点命名标签过长可以使用这个属性来定义文本内容 width: -10, // 宽度减少 10px height: '70%', // 高度为参照元素高度的一半 ellipsis: true, // 文本超出显示范围时,自动添加省略号 breakWord: true, // 是否截断单词 } }, }, markup: [ //组合 { tagName: 'rect', selector: 'body', }, { tagName: 'image', selector: 'image', }, { tagName: 'text', selector: 'text', }, { tagName: 'text', selector: 'label', }, ], data: {}, relation: {}, ports: { ...ports }, //链接桩定义 }, true, ) const imageNodes = imageShapes.map((item) => //呈现画布节点数据的样式 graph.createNode({ shape: 'custom-node', attrs: { image: { 'xlink:href': item.image, }, body: item.body, text: item.label, }, }), ) stencil.load( //载入左侧节点模型库 imageNodes, "processLibrary" );6.定义边的样式(节点连线)
Graph.registerConnector( 'algo-edge', (source, target) => { const offset = 4 const control = 80 const v1 = { x: source.x, y: source.y + offset + control } const v2 = { x: target.x, y: target.y - offset - control } return `M ${source.x} ${source.y} L ${source.x} ${source.y + offset} C ${v1.x} ${v1.y} ${v2.x} ${v2.y} ${target.x} ${target.y - offset} L ${target.x} ${target.y}` }, true, )以及可以在初始化画布graph = new graph({})方法中,定义连线规则
// 连线规则 connecting: { snap: true, // 当 snap 设置为 true 时连线的过程中距离节点或者连接桩 50px 时会触发自动吸附 allowBlank: false, // 是否允许连接到画布空白位置的点,默认为 true allowLoop: false, // 是否允许创建循环连线,即边的起始节点和终止节点为同一节点,默认为 true allowMulti: false, // 当设置为 false 时,在起始和终止节点之间只允许创建一条边 highlight: true, // 拖动边时,是否高亮显示所有可用的连接桩或节点,默认值为 false。 sourceAnchor: { // 当连接到节点时,通过 sourceAnchor 来指定源节点的锚点。 name: 'bottom', args: { dx: 0, }, }, targetAnchor: { // 当连接到节点时,通过 targetAnchor 来指定目标节点的锚点。 name: 'top', args: { dx: 0, }, }, connectionPoint: 'anchor', // 指定连接点,默认值为 boundary。 connector: 'algo-edge', // 连接器将起点、路由返回的点、终点加工为 元素的 d 属性,决定了边渲染到画布后的样式,默认值为 normal。 createEdge() { return graph.createEdge({ attrs: { line: { strokeDasharray: '5 5', stroke: '#808080', strokeWidth: 1, targetMarker: { name: 'block', args: { size: '6', }, }, }, }, }) }, validateMagnet({ magnet }) { return magnet.getAttribute('port-group') !== 'in' }, validateConnection({ sourceView, targetView, sourceMagnet, targetMagnet }) { if (sourceView === targetView) { return false; } if (!sourceMagnet) { return false; } // 只能连接到输入链接桩 if ( !targetMagnet || targetMagnet.getAttribute("port-group") !== "in" ) { return false; } return true; }, // 当停止拖动边的时候根据 validateEdge 返回值来判断边是否生效,如果返回 false, 该边会被清除。 validateEdge({ edge }) { const { source, target } = edge return true } },7.方法们
graph.toJSON() // 数据导出 graph.fromJSON() // 数据渲染 graph.isPannable() // 画布是否可以平移 graph.enablePanning() // 启用画布平移 graph.centerContent(); // 中心对称
8.绑定事件
graph.on('node:added', ({ node, cell }) => {}) // 节点移入画布事件 graph.on("cell:dblclick", ({ node, cell }) => {}); // 节点双击事件 graph.on("node:mouseenter", ({ node }) => { // 节点删除操作 // 鼠标 Hover 节点时添加删除按钮 node.addTools({ name: "button-remove", args: { x: 0, y: 0, offset: { x: 10, y: 10 }, markup: [ //自定义的删除按钮样式 { tagName: 'circle', selector: 'button', attrs: { r: 8, stroke: '#F25C54', strokeWidth: 1, fill: 'rgba(214, 40, 40, 0.25)', cursor: 'pointer', }, }, { tagName: 'text', textContent: '✕', selector: 'icon', attrs: { fill: '#F25C54', fontSize: 7, textAnchor: 'middle', pointerEvents: 'none', y: '0.3em', }, }, ], }, }); }); graph.on("node:removed", ({ node, options }) => { // 删除节点事件 if (!options.ui) { return; } }); graph.on("node:mouseleave", ({ node }) => { // 鼠标移开节点时删除删除按钮 node.removeTools(); }); // 线删除操作 graph.on("edge:mouseenter", ({ edge }) => { // 鼠标 Hover 边时添加删除按钮 edge.addTools([ "target-arrowhead", { name: "button-remove", args: { distance: -30, }, }, ]); }); graph.on("edge:removed", ({ edge, options }) => { // 移除连线事件 if (!options.ui) { return; } const cellId = edge.getTargetCellId() const target = graph.getCellById(cellId)、 if (target) { const id = target.ports.items[0].id target && target.setPortProp(id, 'connected', false) }else{ target && target.setPortProp(cellId+'_in', 'connected', false) } }); graph.on("edge:mouseleave", ({ edge }) => { // 鼠标移开边时删除删除按钮 edge.removeTools(); }); graph.on('node:change:data', ({ node }) => { // 修改节点数据的实时响应事件 node.data = eachNodeData }) graph.on("node:contextmenu", ({ cell, view }) => { // 节点文本 const oldText = cell.attr("text/textWrap/text"); const elem = view.container.querySelector(".x6-edit-text"); if (elem == null) { return; } cell.attr("text/style/display", "none"); if (elem) { elem.style.display = ""; elem.contentEditable = "true"; elem.innerText = oldText; elem.focus(); } const onBlur = () => { cell.attr("text/textWrap/text", elem.innerText); cell.attr("text/style/display", ""); elem.style.display = "none"; elem.contentEditable = "false"; }; elem.addEventListener("blur", () => { onBlur(); elem.removeEventListener("blur", onBlur); }); }); const container = document.getElementById("flowContainer"); graph.on("node:mouseenter",FunctionExt.debounce(() => { // 节点链接桩显隐 const ports = container.querySelectorAll(".x6-port-body"); showPorts(ports, true); }), 500 ); graph.on("node:mouseleave", () => { // 节点链接桩显隐 const ports = container.querySelectorAll(".x6-port-body"); showPorts(ports, false); }); graph.bindKey("backspace", () => { // 点按空格后跳出带有节点的画布区域 const cells = graph.getSelectedCells(); if (cells.length) { graph.removeCells(cells); } });其他有趣的用法
//设置指定路径上的属性值cell.attr('text/text', value) 其中label/text为自定义标题 cell.attr('label/text', state.flinkLabel) cell.attr('label/data', j)9.根据接口数据回显画布流程图
//就是通过这个方法来实现的 graph.fromJSON(nodeData) // 数据渲染,括号内填入回显的数组数据变量 //而nodeData在前面2.提出的数据准备中初始化定义了,我们在接口返回的数据里填充数据和样式就搞定回显了
总结
在vue项目中,使用AntV X6实现节点和画布、连线的配置,非常灵活,一旦会用后有相当多的方法可以使用,自由度和定制度高。还有许多用法可以实现,如点击执行指令显示流程图的动画运行流:
还有自定义的布局等
剩下的其他拓展方法等我下次整理了再发,今天这篇太长了,肝不动了TvT。
参考资料
- ANTV-X6 流程图
- ANTV-X6 快速上手
- 首先我们要了解系统的业务功能需求,以及业务流程的线路是怎样的;