【大数据】HDFS、HBase操作教程(含指令和JAVA API)
目录
1.前言
2.HDFS
2.1.指令操作
2.2.JAVA API
3.HBase
3.1.指令操作
3.2.JAVA API
1.前言
本文是作者大数据专栏系列的其中一篇,前文中已经详细聊过分布式文件系统HDFS和分布式数据库HBase了,本文将会是它们的实操讲解。
HDFS相关前文:
【大数据】分布式文件系统HDFS-CSDN博客
【大数据】大数据概论与Hadoop_大数据导论与hadoop-CSDN博客
HBase相关前文:
【大数据】分布式数据库HBase-CSDN博客
【大数据】分布式数据库HBase下载安装教程-CSDN博客
2.HDFS
2.1.指令操作
创建目录:
hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/mydir
递归创建目录:
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /user/mydir/subdir
上传文件到HDFS:
hdfs dfs -put localfile.txt /user/mydir/
下载文件到本地:
hdfs dfs -get /user/mydir/file.txt localdir/
删除文件:
hdfs dfs -rm /user/mydir/file.txt
递归删除目录:
hdfs dfs -rm -r /user/mydir
查看目录内容:
hdfs dfs -ls /user/mydir
递归查看目录内容:
hdfs dfs -lsr /user/mydir
查看文件详细信息:
hdfs dfs -stat /user/mydir/file.txt
移动或重命名文件:
hdfs dfs -mv /user/mydir/file.txt /user/mydir/newfile.txt
复制文件、目录:
hdfs dfs -cp /user/mydir/file.txt /user/mydir2/
查看文件内容:
hdfs dfs -cat /user/mydir/file.txt
2.2.JAVA API
首先这里有个巨坑:
一定要把core-site.xml里面的fs.defaultFS换成真实IP地址,不能用localhsot
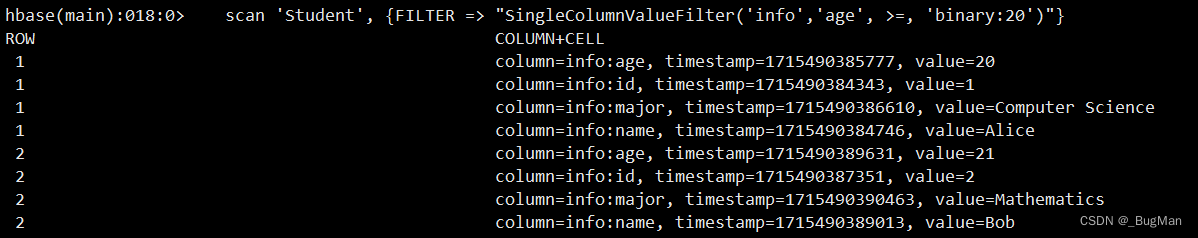
"SingleColumnValueFilter('info','age', >=, 'binary:20')"}
在HBase中,Scan对象用于定义在表上进行扫描时的参数,包括哪些行和列需要被检索,以及如何处理这些数据。Filter是Scan的一部分,用于在服务器端对返回的数据进行过滤,以减少网络传输的数据量,提高查询效率。 Filter类提供了一种方式来指定复杂的过滤逻辑,允许你基于行键(Row Key)、列族、列限定符和时间戳来筛选结果。以下是一些常见的Filter类型及其用法:
-
RowFilter: 用于基于行键的比较,如RowFilter(=, 'binary:rowKey'),匹配特定的行键。
-
SingleColumnValueFilter: 用于基于列族和列限定符的值进行比较,如SingleColumnValueFilter('cf', 'qualifier', CompareOp.GREATER_OR_EQUAL,BinaryComparator.valueOf(Bytes.toBytes(20))),匹配特定列族和列限定符的值大于或等于给定值的行。
-
PrefixFilter: 用于匹配以特定前缀开头的行键,如PrefixFilter(Bytes.toBytes('row-prefix'))。
-
RegexStringComparator: 用于基于正则表达式匹配行键,如RowFilter(CompareOp.EQUAL, RegexStringComparator('.pattern.'))。
-
MultipleColumnPrefixFilter: 用于匹配具有相同前缀的多个列,如MultipleColumnPrefixFilter(Bytes.toBytes('col-prefix'))。
-
PageFilter: 用于限制返回结果的数量,这对于大数据量的扫描很有用,如PageFilter(pageSize),pageSize是你希望一次返回的最大行数。
-
TimestampsFilter: 用于指定返回的行必须包含特定时间戳范围内的版本,如TimestampsFilter(timestamps),timestamps是一个包含多个时间戳的列表。
-
ValueFilter 和 QualifierFilter: 分别基于列值和列限定符进行过滤。
使用不同类型的过滤器的指令示例:
RowFilter(基于行键过滤)
scan 'Student', {FILTER => "RowFilter(=, 'regexstring:^1')"}
SingleColumnValueFilter(基于特定列的值过滤)
scan 'Student', {FILTER => "SingleColumnValueFilter ('info', 'age', >=, 'binary:20')"}
PrefixFilter(基于列前缀过滤)
scan 'Student', {FILTER => "PrefixFilter(Bytes.toBytes('info'))"}
RegexStringComparator(基于列值的正则表达式过滤)
scan 'Student', {FILTER => "RowFilter(=, 'regexstring:.Alice.')"}
MultipleColumnPrefixFilter(基于多列前缀过滤)
scan 'Student', {FILTER => "MultipleColumnPrefixFilter(Bytes.toBytes('info'))"}
ValueFilter(基于列值的比较过滤)
scan 'Student', {FILTER => "ValueFilter(=, 'binary:Alice')"}
QualifierFilter(基于列限定符的比较过滤)
scan 'Student', {FILTER => "QualifierFilter(=, 'binary:age')"}
清理表:
delete 'Student', '1' delete 'Student', '2' delete 'Student', '3' disable 'Student' drop 'Student'
3.2.JAVA API
HBase也要注意和HDFS中相似的问题,hbase-site.xml中也要用真实的IP地址,不然JAVA API的Client端和HBase不在一台机器上的会,就会访问不到HBase,下面的代码中作为演示代码并没有用真实IP,仍然用的LocalHost,这点要注意。
依赖:
org.apache.hbase
hbase-client
2.2.2
代码示例:
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableName; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Connection; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.ConnectionFactory; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Delete; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Get; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Result; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Table; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes; public class HBaseExample { public static void main(String[] args) { Configuration config = HBaseConfiguration.create(); config.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "localhost"); // 设置ZooKeeper地址 config.set("hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort", "2181"); // 设置ZooKeeper端口 try (Connection connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(config); Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("students"))) { // 创建表 table.createIfNotExists(); // 插入数据 Put put1 = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("student1")); put1.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("Alice")); put1.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("age"), Bytes.toBytes("20")); put1.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("major"), Bytes.toBytes("CS")); table.put(put1); Put put2 = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("student2")); put2.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("Bob")); put2.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("age"), Bytes.toBytes("21")); put2.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("major"), Bytes.toBytes("Math")); table.put(put2); // 查询数据 Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes("student1")); Result result = table.get(get); System.out.println("Name: " + Bytes.toString(result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name")))); System.out.println("Age: " + Bytes.toInt(result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("age")))); System.out.println("Major: " + Bytes.toString(result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("major")))); // 根据条件删除数据 Delete delete = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes("student1")); table.delete(delete); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }