深度解析 Spring 源码:揭秘 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 的 Bean 生命周期处理
文章目录
- 一、AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 概述
- 1.1 详细分析
- 1.2 设计思想
- 二、深入解析AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 的实现细节
- 2.1 Bean 实例化过程分析
- 2.1.1 createBean()
- 2.1.2 createBeanInstance()
- 2.2 Bean 属性注入的实现机制
- 2.2.1 populateBean()
- 2.2.2 applyBeanPropertyValues()
- 2.3 初始化方法的调用过程
- 2.3.1 initializeBean()
- 2.3.2 invokeAwareMethods()
- 2.3.4 applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization()
- 2.3.5 invokeInitMethods()
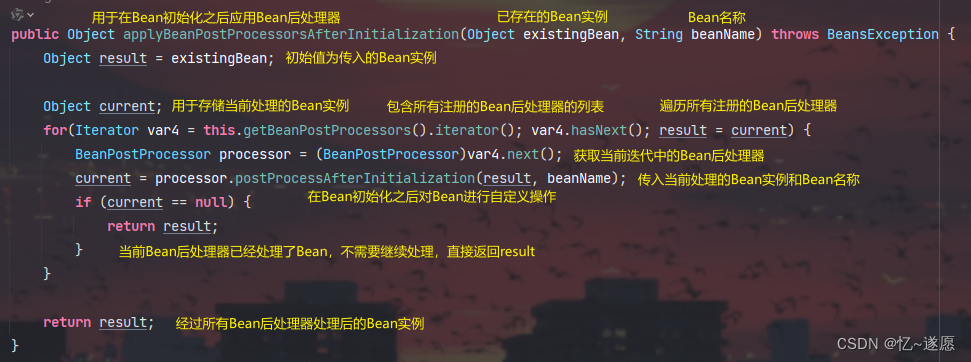
- 2.3.6 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization()
- 2.4 销毁机制的实现
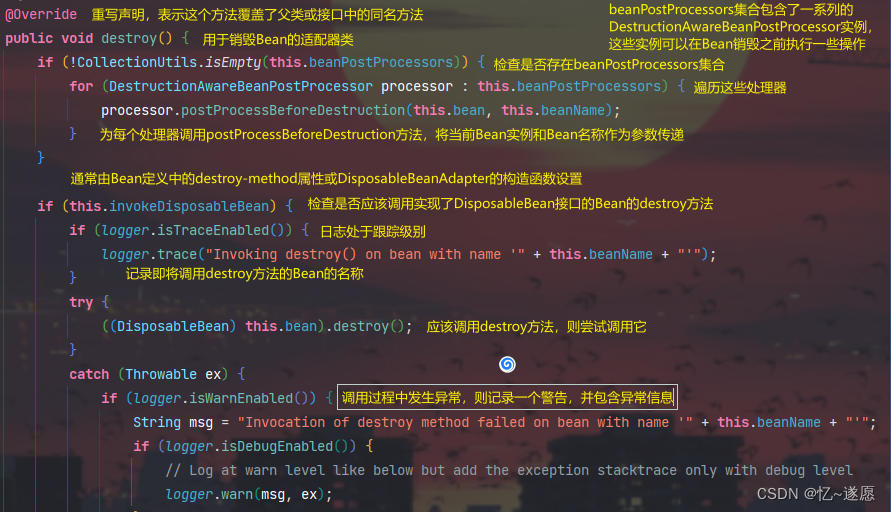
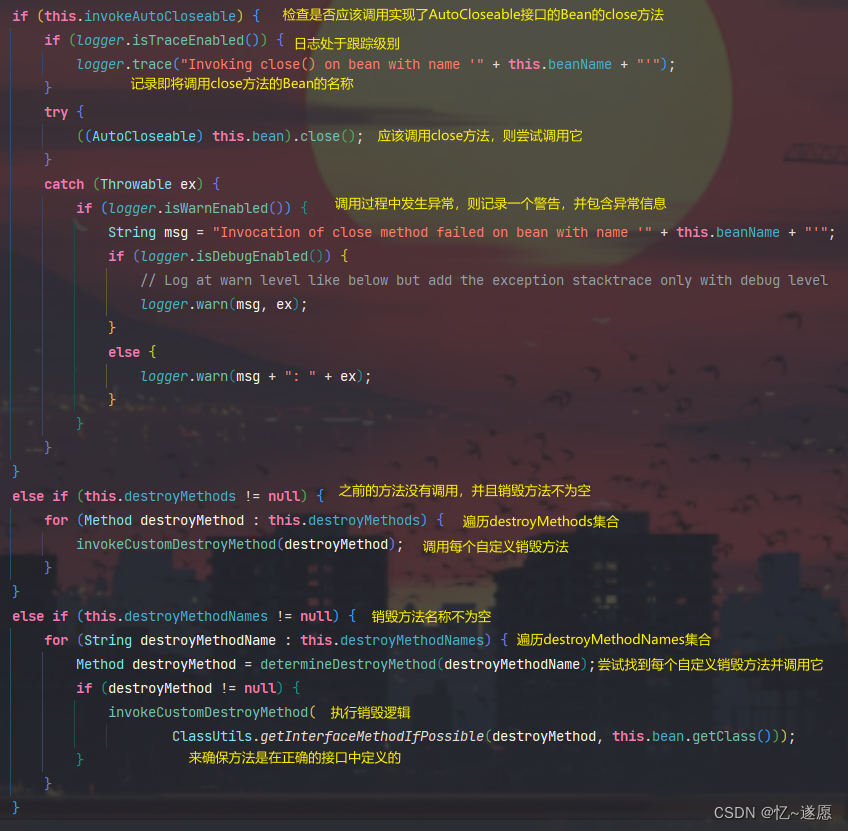
- 2.4.1 destroyBean()
- 2.4.2 destroy()
- 三、实例分析与应用场景
- 3.1 如何利用 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 扩展 Bean 的功能
- 3.2 在项目中如何充分利用 Bean 生命周期处理机制
一、AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 概述
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory是Spring框架中的一个重要类,主要负责实现Bean的自动装配功能。
1.1 详细分析
- BeanFactory和AutowireCapableBeanFactory: 在Spring中,BeanFactory是IoC容器的基础接口,负责管理bean的生命周期和依赖注入。AutowireCapableBeanFactory是BeanFactory的子接口,扩展了自动装配功能,可以根据配置自动解析和注入bean的依赖关系。
- AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的作用: AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory是AutowireCapableBeanFactory接口的抽象实现类。它提供了一系列用于自动装配和创建bean的模板方法,包括:
- 解析bean的依赖关系,根据需要进行自动装配。
- 执行属性填充,将依赖注入到bean中。
- 初始化bean,包括调用初始化方法和应用BeanPostProcessors(后置处理器)等。
- 关键方法和功能: AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory中的关键方法包括:
- createBean(Class beanClass):根据给定的类创建一个新的bean实例。
- applyBeanPropertyValues(Object existingBean, String beanName):应用属性值到现有的bean实例。
- initializeBean(Object existingBean, String beanName):初始化bean实例,包括执行初始化方法和应用后置处理器等。
- 自动装配:该类实现了自动装配功能,根据bean的依赖关系和配置,自动解析和注入所需的依赖。自动装配可以通过构造函数、设值方法或字段进行。
1.2 设计思想
- IoC和 DI: Spring 框架的核心思想之一是 IoC 和 DI。IoC 意味着将控制权交给框架,由框架负责管理对象的生命周期和依赖关系。DI 则是 IoC 的一种具体实现方式,通过依赖注入的方式,将对象的依赖关系从代码中解耦,使得代码更加灵活和可维护。AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 实现了这一设计思想,通过自动装配的方式,实现了对象之间的依赖注入。
- 面向接口编程: Spring 框架鼓励面向接口编程,而不是面向实现编程。AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 提供了一系列接口,如 BeanFactory、AutowireCapableBeanFactory 等,通过面向接口编程的方式,提高了代码的可扩展性和灵活性。
- 模板方法模式: AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 使用了模板方法模式,定义了一组抽象方法和基本方法,子类可以根据具体需求来实现这些抽象方法,从而实现不同的自动装配策略。
- 单一职责原则: 设计思想中的单一职责原则要求一个类应该只有一个引起它变化的原因。AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 的设计遵循了这一原则,它专注于实现 Bean 的自动装配功能,而将其他功能如 Bean 的创建、初始化等交给了父类 AbstractBeanFactory 来实现,从而使得类的职责更加清晰和单一。
二、深入解析AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 的实现细节
本文主要详解Bean生命周期的核心实现方法,过程有些缺少,想要了解的Bean生命周期全过程的读者,可以查看我上一篇文章。
2.1 Bean 实例化过程分析
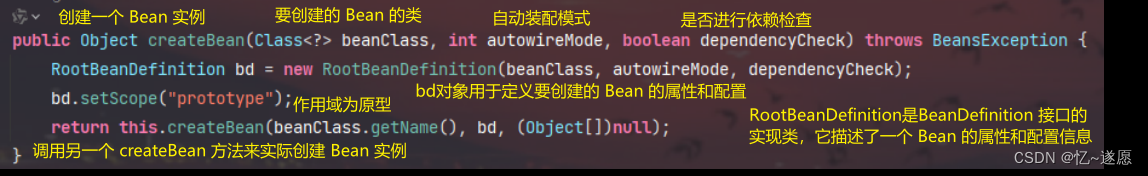
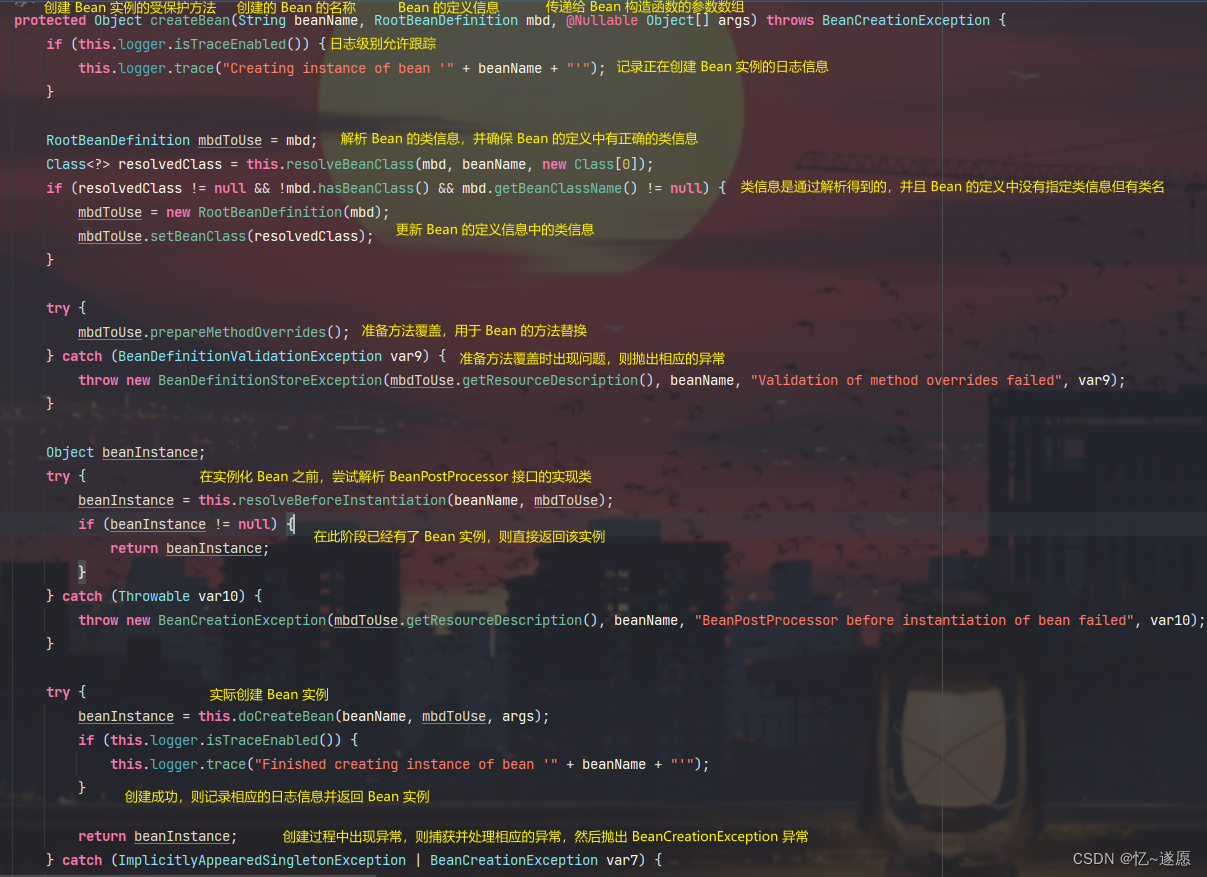
2.1.1 createBean()
根据提供的类信息和配置创建一个新的 Bean 实例,并将其作用域设置为原型模式。
主要负责 Bean 实例的创建过程,包括解析类信息、准备方法覆盖、实例化前的处理以及实际的 Bean 创建过程。
2.1.2 createBeanInstance()
主要负责创建 Bean 实例,体现Spring在实例化Bean时考虑的各种情况,包括是否需要自动装配,构造方法是否已经解析,以及如何选择合适的构造方法来创建Bean实例
2.2 Bean 属性注入的实现机制
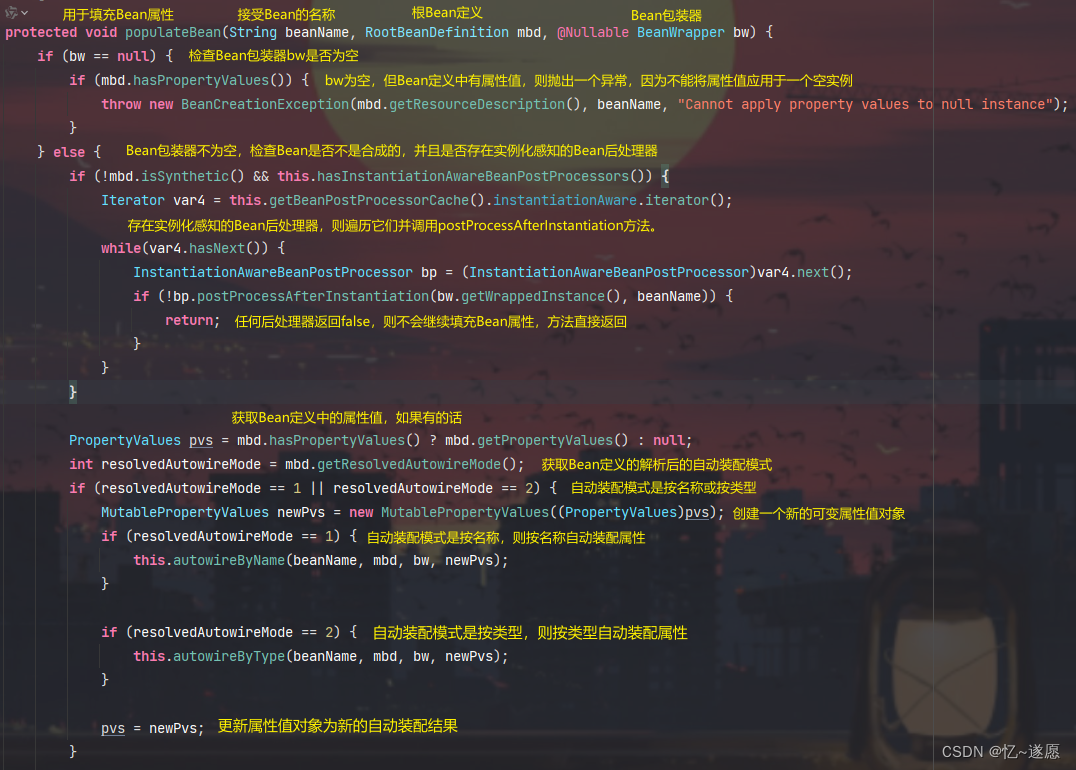
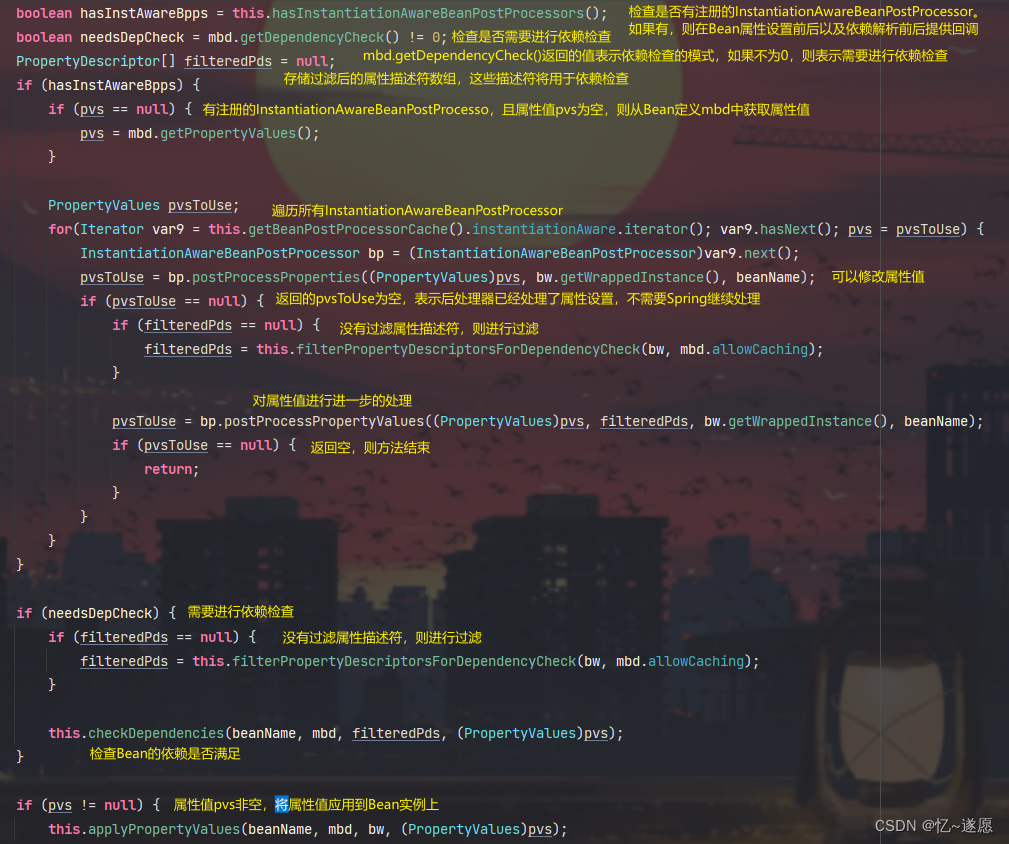
2.2.1 populateBean()
主要负责填充Bean属性的populateBean方法,负责处理Bean的属性值,包括自动装配和依赖检查。
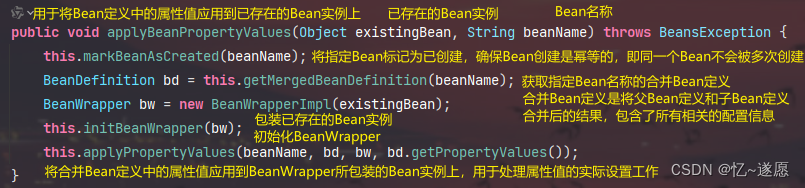
2.2.2 applyBeanPropertyValues()
主要用于将Bean定义中的属性值应用到已存在的Bean实例上的方法。
2.3 初始化方法的调用过程
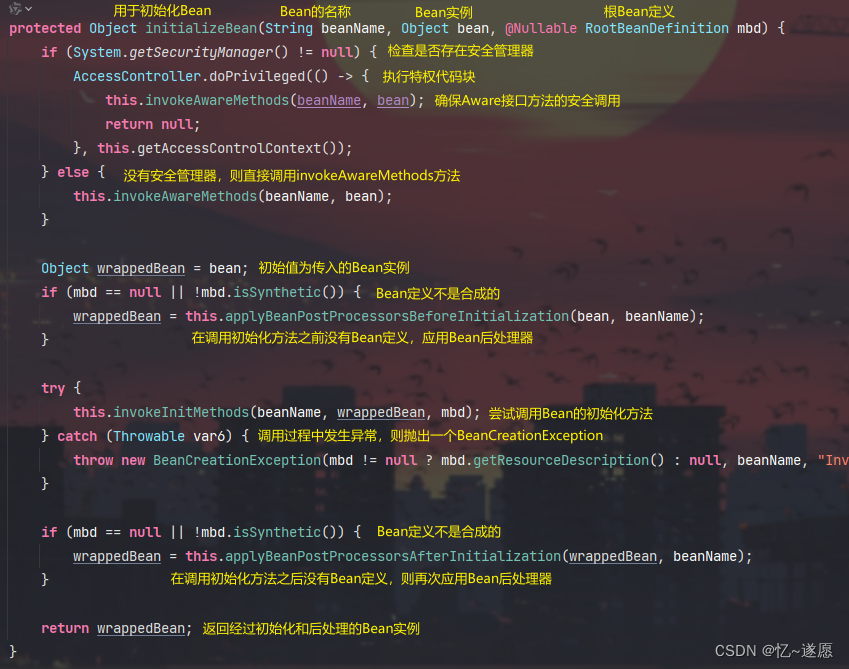
2.3.1 initializeBean()
负责初始化Bean,调用Bean生命周期中的回调方法,包括Aware接口方法和自定义的初始化方法。
2.3.2 invokeAwareMethods()
确保了实现了Aware接口的Bean,可以在其生命周期中获得对Spring容器的相关信息的访问。
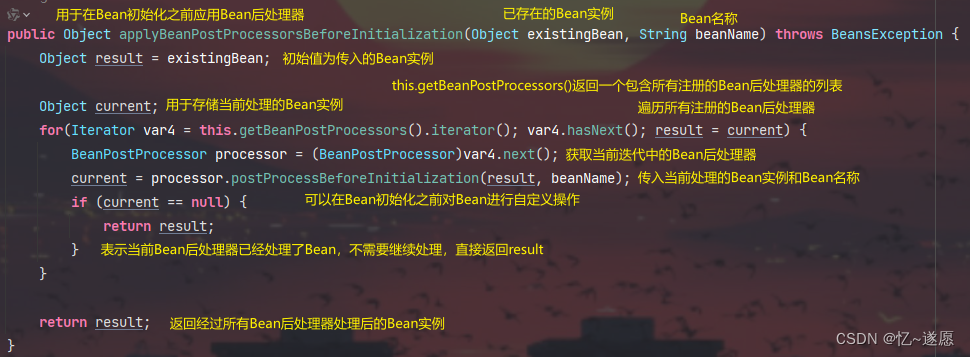
2.3.4 applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization()
确保了在Bean初始化之前,所有的Bean后处理器都有机会对Bean进行自定义操作。
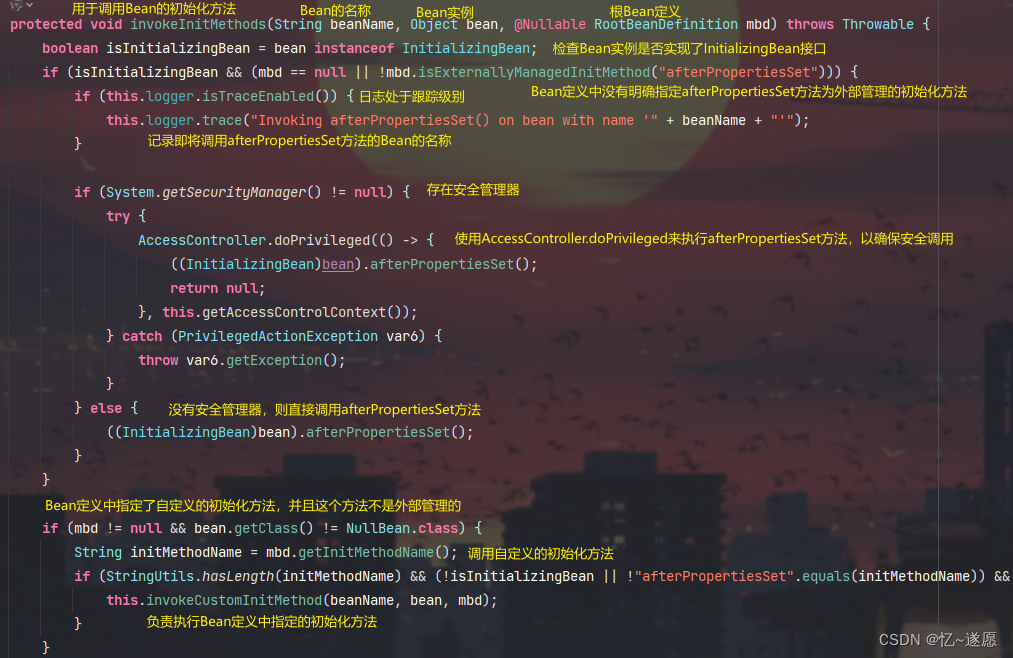
2.3.5 invokeInitMethods()
确保了Bean在初始化过程中可以执行自定义的逻辑,包括实现InitializingBean接口的Bean的afterPropertiesSet方法和Bean定义中指定的自定义初始化方法。
2.3.6 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization()
确保了在Bean初始化之后,所有的Bean后处理器都有机会对Bean进行自定义操作。
2.4 销毁机制的实现
2.4.1 destroyBean()
确保了Bean在销毁过程中可以执行自定义的逻辑,包括实现DisposableBean接口的Bean的destroy方法和Bean定义中指定的自定义销毁方法。
2.4.2 destroy()
负责调用实现了DisposableBean接口的Bean的destroy方法,以及Bean定义中指定的自定义销毁方法。
三、实例分析与应用场景
3.1 如何利用 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 扩展 Bean 的功能
要利用AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory扩展Bean的功能,可以通过编写自定义的BeanPostProcessor或BeanFactoryPostProcessor来实现。这两个接口允许在Spring容器实例化和配置Bean的不同阶段介入并添加自定义逻辑。例如,可以在Bean初始化前后执行额外的操作,或者在Bean实例化前修改Bean的定义。
使用BeanPostProcessor来扩展Bean功能的Demo:
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * CustomBeanPostProcessor实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,并覆盖了postProcessBeforeInitialization和postProcessAfterInitialization方法 * 这两个方法分别在Bean初始化之前和之后执行 * 可以在这些方法中添加自定义的逻辑,以扩展Bean的功能 */ @Component public class CustomBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { /** * 日常开发中:可以执行额外的初始化操作,例如初始化某些属性、连接到外部资源或设置日志记录器等 */ @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { // 在Bean初始化之前执行操作 if (bean instanceof CustomBean) { ((CustomBean) bean).beforeInit(); // 假设CustomBean有一个beforeInit方法 } return bean; } /** * 日常开发中:可以执行额外的销毁操作,例如释放资源、关闭连接或记录统计信息等 */ @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { // 在Bean初始化之后执行操作 if (bean instanceof CustomBean) { ((CustomBean) bean).afterInit(); // 假设CustomBean有一个afterInit方法 } return bean; } }使用BeanFactoryPostProcessor扩展Bean功能的Demo:
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * CustomBeanFactoryPostProcessor实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口 * 在postProcessBeanFactory方法中注册了一个名为"customBean"的新Bean */ @Component public class CustomBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor { /** * 日常开发中:修改Bean定义等 */ @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { // 在这里可以访问和修改Bean的定义 // 如:添加一个新的Bean定义 beanFactory.registerSingleton("customBean", new CustomBean()); } }3.2 在项目中如何充分利用 Bean 生命周期处理机制
案例:有一个简单的Spring Boot项目,其中包含一个名为UserService的服务类,以及一个名为CustomBean的自定义Bean类。将通过自定义初始化和销毁逻辑、AOP、事件监听器和与外部资源的连接来展示如何充分利用Bean生命周期处理机制。
CustomBean自定义Bean类:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; import javax.annotation.PreDestroy; /** * 演示自定义初始化和销毁逻辑 */ @Component public class CustomBean { @PostConstruct public void init() { System.out.println("CustomBean initialized"); // 添加自定义的初始化逻辑... } @PreDestroy public void destroy() { System.out.println("CustomBean destroyed"); // 添加自定义的销毁逻辑... } }CustomBeanPostProcessor类:
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * 实现BeanPostProcessor接口,以便在Bean的初始化和销毁阶段添加自定义逻辑 */ @Component public class CustomBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean instanceof CustomBean) { ((CustomBean) bean).init(); } return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean instanceof CustomBean) { ((CustomBean) bean).destroy(); } return bean; } }CustomAspect切面类:
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Aspect @Component public class CustomAspect { @After("execution(* com.example.UserService.*(..))") public void afterUserServiceMethods() { System.out.println("AOP: After UserService methods"); // 添加横切关注点... } }CustomApplicationListener类:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; import org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * 实现ApplicationListener接口,以便监听Bean生命周期事件 */ @Component public class CustomApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener { @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) { System.out.println("ApplicationListener: Context refreshed"); // 监听器逻辑... } }UserService中使用外部资源(例如数据库连接):
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; import javax.annotation.PreDestroy; @Service public class UserService { @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; @PostConstruct public void init() { System.out.println("UserService initialized"); // 连接到外部资源... } public void createUser(String username) { System.out.println("Creating user: " + username); // 业务逻辑... } public void deleteUser(String username) { System.out.println("Deleting user: " + username); // 业务逻辑... } @PreDestroy public void destroy() { System.out.println("UserService destroyed"); // 释放外部资源... } }山的那边有我的期许,你有看见吗