芋道SpringBoot配置Maven、创建SpringBoot项目、创建Web接口、读取配置信息
🌹作者主页:青花锁 🌹简介:Java领域优质创作者🏆、Java微服务架构公号作者😄
🌹简历模板、学习资料、面试题库、技术互助
🌹文末获取联系方式 📝
系列文章目录
第一章 芋道 Spring Boot 快速入门
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- 1、芋道网站
- 2、下载和安装maven工具
- 3、第一个SpringBoot 项目
- 3.1、初始化项目
- 3.2、配置maven
- 3.3、启动项目
- 3.4、定义一个hello world接口
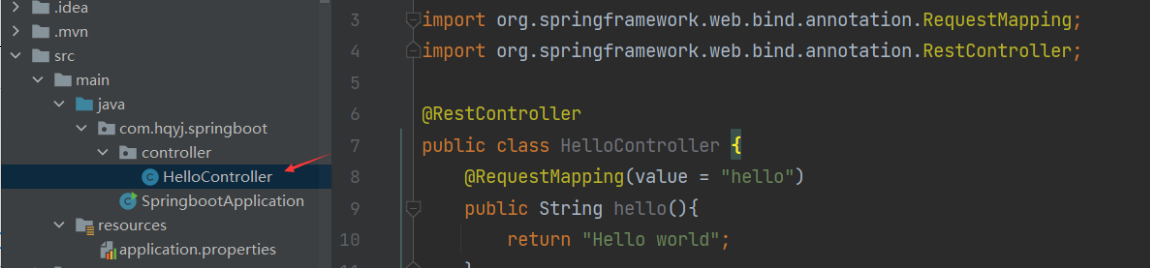
- 3.4.1、在Controller包下创建类,并编写hello world接口
- 3.4.2、通过浏览器访问接口
- 3.5、解决接口跨域问题
- 3.5.1、类或方法解决接口跨域问题
- 3.5.2、配置全局跨域
- 4、接收参数
- 4.1、通过HttpServletRequest 接收参数
- 4.2、通过@RequestParam接收参数
- 4.3、通过@PathVariable 接收参数
- 4.4、通过@RequestBody 接收参数
- 5、starter机制
- 6、YAML标记语言
- 6.1、application.properties
- 6.2、application.yml
- 6.2.1、YAML 简介
- 6.2.2、YYAML 支持以下三种数据结构
- 6.2.2.1、对象:键值对的集合
- 6.2.2.2、数组:一组按次序排列的值
- 6.2.2.3、字面量:单个的、不可拆分的值
- 7、配置文件与JavaBean绑定
- 7.1、使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解
- 7.2、使用 @Value 注解
- 7.3、@Value 与 @ConfigurationProperties 对比
- 7.3.1、 使用位置不同
- 7.3.2、功能不同
- 7.3.3、松散绑定支持不同@ConfigurationProperties:支持松散绑定(松散语法),例如实体类 Person 中有一个属性为 firstName,那么配置文件中的属性名支持以下写法:
- 7.3.4、 SpEL 支持不同
- 7.3.5、复杂类型封装
- 7.3.6、应用场景不同
- 7.4、非application配置文件
- 往期热门专栏回顾
前言
芋道 SpringBoot是一款国产的SpringCloud微服务框架,包括Outh2.0、微服务网关、微服务注册中心、配置中心、消息队列、任务调度、链路追踪、服务保障等。
今天介绍下芋道 SpringBoot入门,包括SpringBoot介绍、第一个SpringBoot案例,所需要下载安装的基础工具等。
1、芋道网站
源码分析首页:https://www.iocoder.cn/
芋道 SpringBoot快速入门章:https://www.iocoder.cn/Spring-Boot/quick-start/?github
下面是我自己整理的Spingboot、微服务学习专栏,从Spingboot 零基础到微服务实战。
SpringBoot框架学习专栏:https://blog.csdn.net/s445320/category_12273537.html
SpringCloud微服务学习专栏 :https://blog.csdn.net/s445320/category_12439818.html
微服务实战专栏:https://blog.csdn.net/s445320/category_12345409.html
2、下载和安装maven工具
https://maven.apache.org/download.cgi
常用版本3:https://dlcdn.apache.org/maven/maven-3(只有最新的几个版本)
更新下载站:https://archive.apache.org/dist/maven/maven-3/ (包含从3.0 到 3.9的大多数版本)
下载解压,修改conf下的setting.xml,优先从阿里云镜像拉取关联包
alimaven aliyun maven http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/ central maven.net.cn oneof the central mirrors in china http://maven.net.cn/content/groups/public/ central central Maven Repository Switchboard http://repo1.maven.org/maven2/ central修改本地maven库路径
d:\localRepository
3、第一个SpringBoot 项目
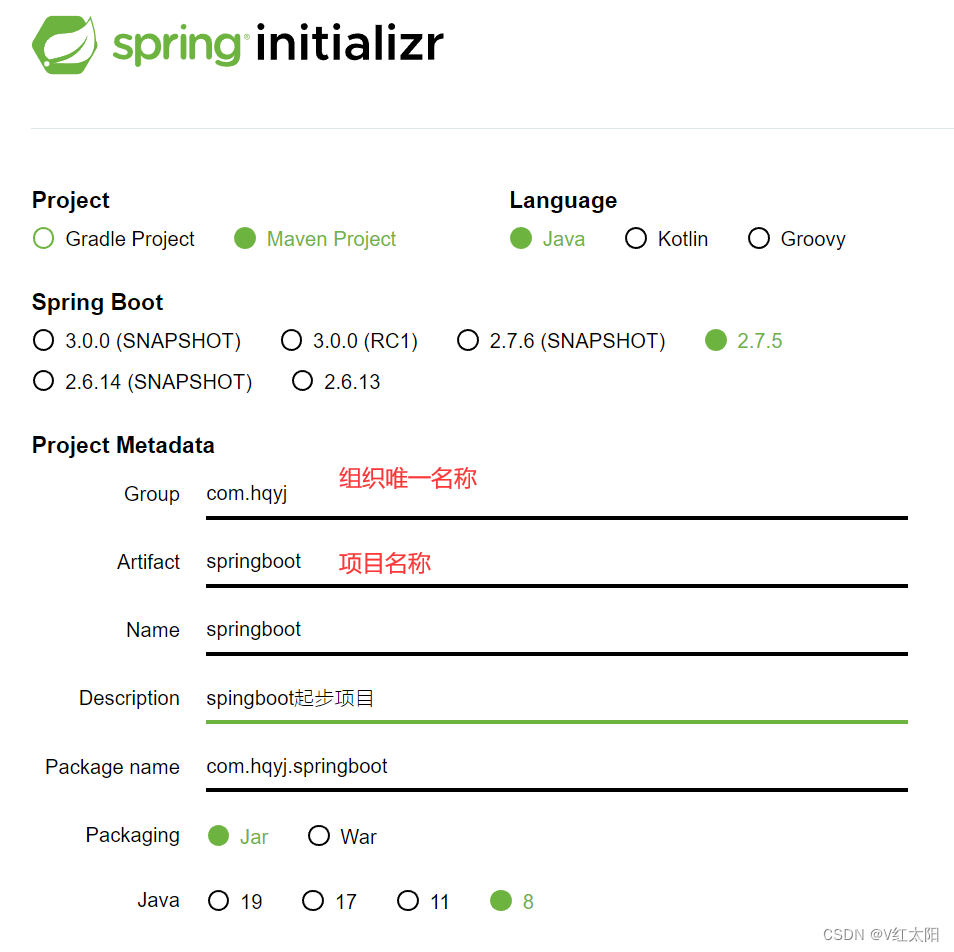
3.1、初始化项目
https://start.spring.io/
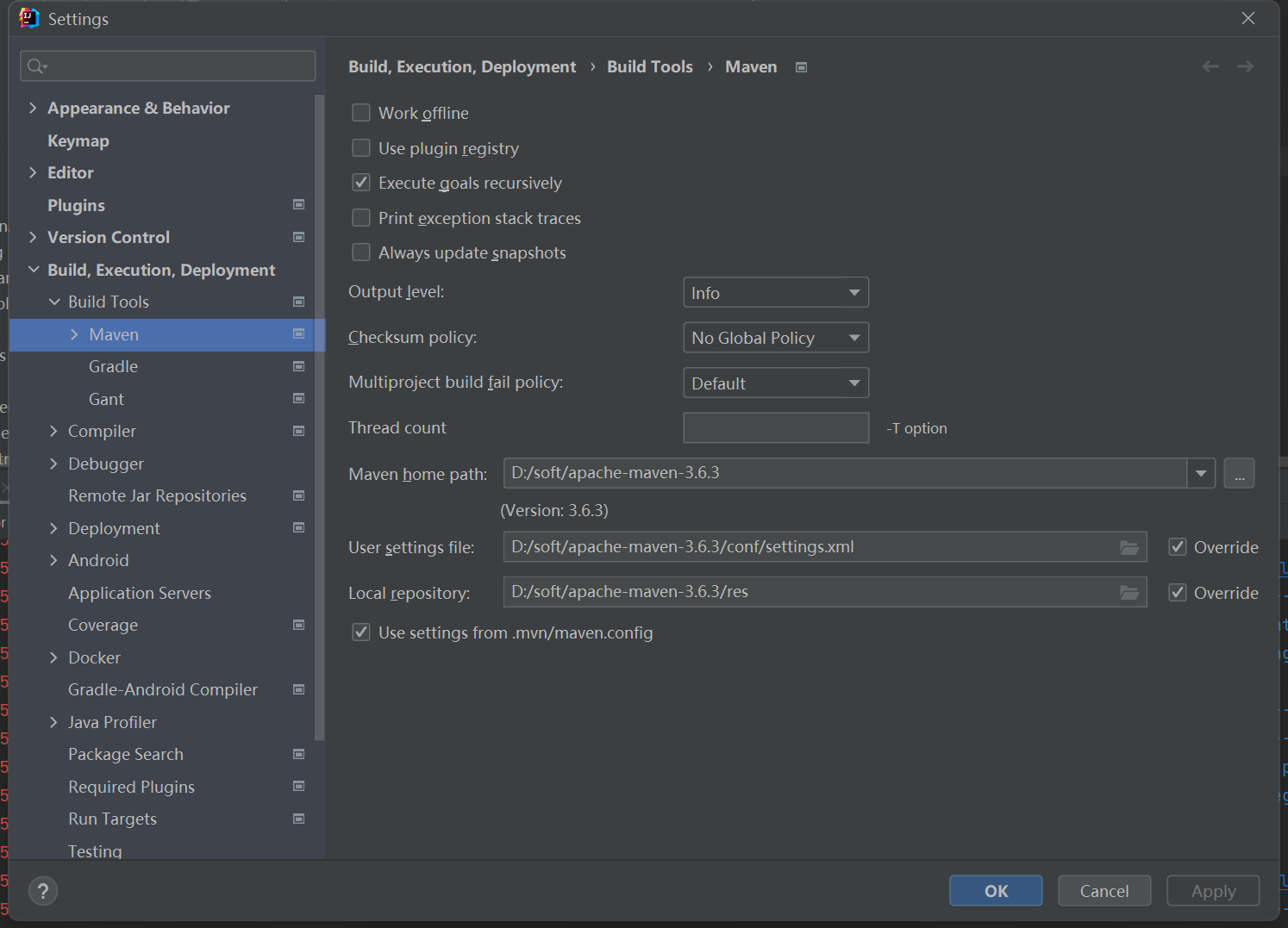
3.2、配置maven
3.3、启动项目
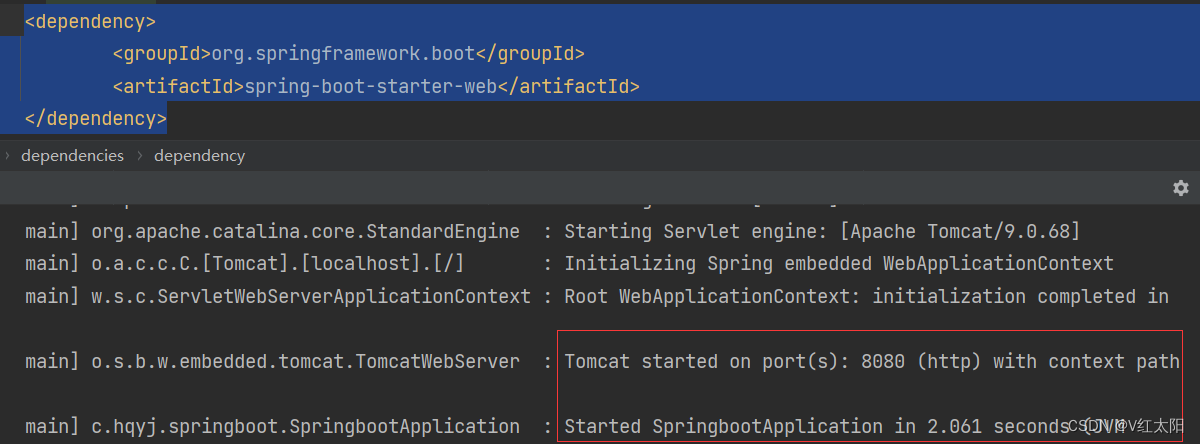
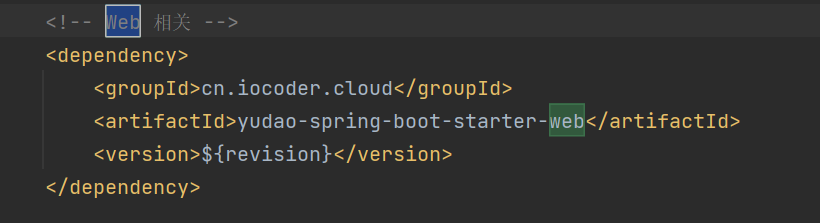
在pom.xml添加web依赖,集成内嵌tomcat
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web3.4、定义一个hello world接口
3.4.1、在Controller包下创建类,并编写hello world接口
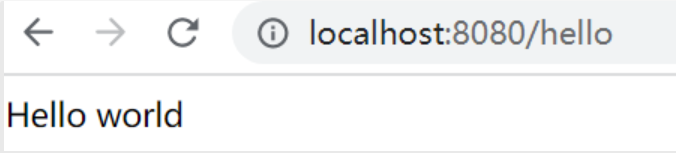
3.4.2、通过浏览器访问接口
地址:http://localhost:8080/hello
3.5、解决接口跨域问题
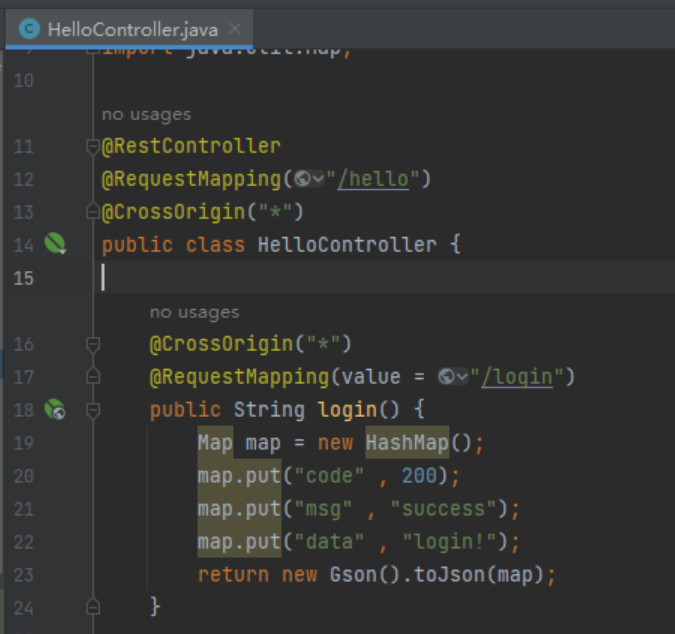
3.5.1、类或方法解决接口跨域问题
1、在class或method上加上【@CrossOrigin(“*”)】,解决跨域问题
3.5.2、配置全局跨域
新建【config】package,添加自定义的跨域java文件
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer; @Configuration public class MyWebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) { registry.addMapping("/**") .allowedHeaders("*") .allowedMethods("*") .maxAge(1800) .allowedOrigins("*"); } }4、接收参数
4.1、通过HttpServletRequest 接收参数
前端访问路径:http://127.0.0.1/user/login?userName=zs&pwd=123
后端Java代码:
@RequestMapping("/login") public Map login(HttpServletRequest request , HttpServletResponse response) { // URL: http://127.0.0.1/user/login?userName=zs&pwd=123 Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("code" , 200); map.put("msg" , "success"); //第一种方式接收入参 String userName = request.getParameter("userName"); String pwd = request.getParameter("pwd"); return map; }4.2、通过@RequestParam接收参数
前端访问路径:http://127.0.0.1/user/login?userName=zs&pwd=123
后端Java代码:
@RequestMapping("/login") public Map login(@RequestParam(value="name" ,required=true) String userName, @RequestParam(value="pwd" ,required=true) String password, HttpServletResponse response) { // @RequestParam(value="name" ,required=true) required=true传入的值不允许为空 // URL: http://127.0.0.1/user/login?userName=zs&pwd=123 //第二种方式接收入参 System.out.println(userName + "||" + password); Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("code" , 200); map.put("msg" , "success"); return map; }4.3、通过@PathVariable 接收参数
前端访问路径:http://127.0.0.1/user/logintwo/zs/123
后端Java代码:
@RequestMapping("/logintwo/{userName}/{pwd}") public Map loginTwo(@PathVariable String userName, @PathVariable String pwd) { // URL: http://127.0.0.1/user/logintwo/zs/123 //第三种方式接收入参 System.out.println(userName + "||" + pwd); Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("code" , 200); map.put("msg" , "success"); return map; }4.4、通过@RequestBody 接收参数
前端JavaScript代码:
//针对@RequestBody 接收入参的前端ajax请求 $.ajax({ url: "http://localhost:8089/api/Home", data: JSON.stringify(obj), method: "post", dataType: "json", contentType: 'application/json', success: function (data) { console.log(data) if (data.code == 200) { alert("登录成功"); } else { alert("登录失败:" + data.msg); } }后端Java代码:
@PostMapping("/register") public Map register(@RequestBody User user) { // URL: http://127.0.0.1/user/register/ // {userName:xxx,pwd:xxx} //第四种方式接收入参 System.out.println(new Gson().toJson(user) ); Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("code" , 200); map.put("msg" , "success"); return map; }5、starter机制
starter 中整合了该场景下各种可能用到的依赖,用户只需要在 Maven 中引入 starter 依赖,SpringBoot 就能自动扫描到要加载的信息并启动相应的默认配置
比如:
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-parent 2.6.13Spring Boot 项目可以通过继承 spring-boot-starter-parent 来获得一些合理的默认配置,它主要提供了以下特性:
- 默认 JDK 版本(Java 8)
- 默认字符集(UTF-8)
- 依赖管理功能
- 资源过滤
- 默认插件配置
- 识别 application.properties 和 application.yml 类型的配置文件
6、YAML标记语言
springBoot 默认使用以下 2 种全局的配置文件,其文件名是固定的。
6.1、application.properties
server.port= 8081
6.2、application.yml
server: port: 8081
6.2.1、YAML 简介
YAML 全称 YAML Ain’t Markup Language,比xml更适合做配置文件
YAML 的语法如下:
- 使用缩进表示层级关系。
- 缩进时不允许使用 Tab 键,只允许使用空格。
- 缩进的空格数不重要,但同级元素必须左侧对齐。
- 大小写敏感。
比如:
server: port: 8081 spring: profiles: dev datasource: url: xxxxxxxxx
6.2.2、YYAML 支持以下三种数据结构
6.2.2.1、对象:键值对的集合
使用缩进表示对象与属性的层级关系
user: name: Kelvin gender: 男行内写法:
user: {name: Kelvin,gender: 男}6.2.2.2、数组:一组按次序排列的值
使用-表示集合元素
hobbyList: - run - badminton - mountain climb
或
hobbyList: [run,badminton,mountain climb]
使用,表示数组元素
hobbies:run,badminton,mountain climb
6.2.2.3、字面量:单个的、不可拆分的值
数值、日期、字符串等
YAML组织结构:一个文件可有多个文档组成,文档之间用“—”分隔
7、配置文件与JavaBean绑定
SpringBoot 提供了以下 2 种方式进行配置绑定:
7.1、使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解
定义JavaBean
user: userName: Kelvin gender: 男 # 对应的Bean文件里的数组 hobbies: run, badminton, mountainclimb # 对应的Bean文件里的List hobbyList: - run - badminton - mountainclimbimport lombok.Data; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.List; /** * 用户实体类 */ @Data @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user") public class User { /** * 名字 */ // @Value("${user.userName}") private String userName; /** * 性别 */ // @Value("${user.gender}") private String gender; /** * 爱好 */ // @Value("${user.hobbies}") private String[] hobbies; /** * 爱好 */ private List hobbyList; public User() { } }@SpringBootTest class SpringbootApplicationTests { /** * 用户实体类对象 */ @Autowired private User user; @Test void contextLoads() { System.out.println("#############user: " + user); } }打印日志:#############user: User{name=‘Kelvin’, gender=‘男’, hobbies=[run, badminton, mountainclimb]}
7.2、使用 @Value 注解
/** * 用户实体类 */ @Component public class User { /** * 名字 */ @Value("${user.userName}") private String userName; /** * 性别 */ @Value("${user.gender}") private String gender; /** * 爱好 */ private String[] hobbies; }7.3、@Value 与 @ConfigurationProperties 对比
7.3.1、 使用位置不同
- @ConfigurationProperties:标注在 JavaBean 的类名上;
- @Value:标注在 JavaBean 的属性上。
7.3.2、功能不同
- @ConfigurationProperties:用于批量绑定配置文件中的配置;
- @Value:只能一个一个的指定需要绑定的配置。
7.3.3、松散绑定支持不同@ConfigurationProperties:支持松散绑定(松散语法),例如实体类 Person 中有一个属性为 firstName,那么配置文件中的属性名支持以下写法:
- person.firstName
- person.first-name
- person.first_name
- PERSON_FIRST_NAME
@Vaule:不支持松散绑定。
7.3.4、 SpEL 支持不同
- @ConfigurationProperties:不支持 SpEL 表达式;
- @Value:支持 SpEL 表达式。
7.3.5、复杂类型封装
- @ConfigurationProperties:支持所有类型数据的封装,例如 Map、List、Set、以及对象等;
- @Value:只支持基本数据类型的封装,例如字符串、布尔值、整数等类型。
7.3.6、应用场景不同
@Value 和 @ConfigurationProperties 两个注解之间,并没有明显的优劣之分,它们只是适合的应用场景不同而已。
- 若只是获取配置文件中的某项值,则推荐使用 @Value 注解;
- 若专门编写了一个 JavaBean 来和配置文件进行映射,则建议使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解。
7.4、非application配置文件
@PropertySource(value =“classpath:userinfo.properties”)
定义配置文件
user.userName=Tiger user.gender=男 user.hobbies=run,badminton,mountainclimb
往期热门专栏回顾
专栏 描述 Java项目实战 介绍Java组件安装、使用;手写框架等 Aws服务器实战 Aws Linux服务器上操作nginx、git、JDK、Vue Java微服务实战 Java 微服务实战,Spring Cloud Netflix套件、Spring Cloud Alibaba套件、Seata、gateway、shadingjdbc等实战操作 Java基础篇 Java基础闲聊,已出HashMap、String、StringBuffer等源码分析,JVM分析,持续更新中 Springboot篇 从创建Springboot项目,到加载数据库、静态资源、输出RestFul接口、跨越问题解决到统一返回、全局异常处理、Swagger文档 Spring MVC篇 从创建Spring MVC项目,到加载数据库、静态资源、输出RestFul接口、跨越问题解决到统一返回 华为云服务器实战 华为云Linux服务器上操作nginx、git、JDK、Vue等,以及使用宝塔运维操作添加Html网页、部署Springboot项目/Vue项目等 Java爬虫 通过Java+Selenium+GoogleWebDriver 模拟真人网页操作爬取花瓣网图片、bing搜索图片等 Vue实战 讲解Vue3的安装、环境配置,基本语法、循环语句、生命周期、路由设置、组件、axios交互、Element-ui的使用等 Spring 讲解Spring(Bean)概念、IOC、AOP、集成jdbcTemplate/redis/事务等 资料获取,更多粉丝福利,关注下方公众号获取