【C++】List模拟实现
💞💞 前言
hello hello~ ,这里是大耳朵土土垚~💖💖 ,欢迎大家点赞🥳🥳关注💥💥收藏🌹🌹🌹
💥个人主页:大耳朵土土垚的博客
💥 所属专栏:C++入门至进阶
这里将会不定期更新有关C++的内容,希望大家多多点赞关注收藏💖💖
目录
- 💞💞 前言
- 一、什么是List
- 二、Lits模拟实现
- 2.1 List完整实现代码
- 2.2List框架
- ✨ListNode节点
- ✨List类
- 2.3尾插尾删
- 2.4迭代器封装
- ✨尾插尾删测试代码
- ✨const迭代器
- 2.5头插头删
- ✨头插头删测试代码
- 2.6任意位置插入
- 2.7任意位置删除
- ✨任意位置插入删除测试代码
- 2.8清空数据
- 2.9析构函数
- 2.10构造函数
- ✨默认构造
- ✨拷贝构造
- ✨initializer_list构造
- ✨测试代码
- 2.11赋值运算符重载
- ✨赋值运算符重载测试代码
- 三、结语
一、什么是List
C++中的list是一种双向链表(doubly linked list)的实现。它是C++标准库中的一种容器,可以存储一系列元素,并且允许在任意位置插入、删除和访问元素。对于双向链表有疑问的可以点击查看数据结构——带头双向循环链表详解
二、Lits模拟实现
2.1 List完整实现代码
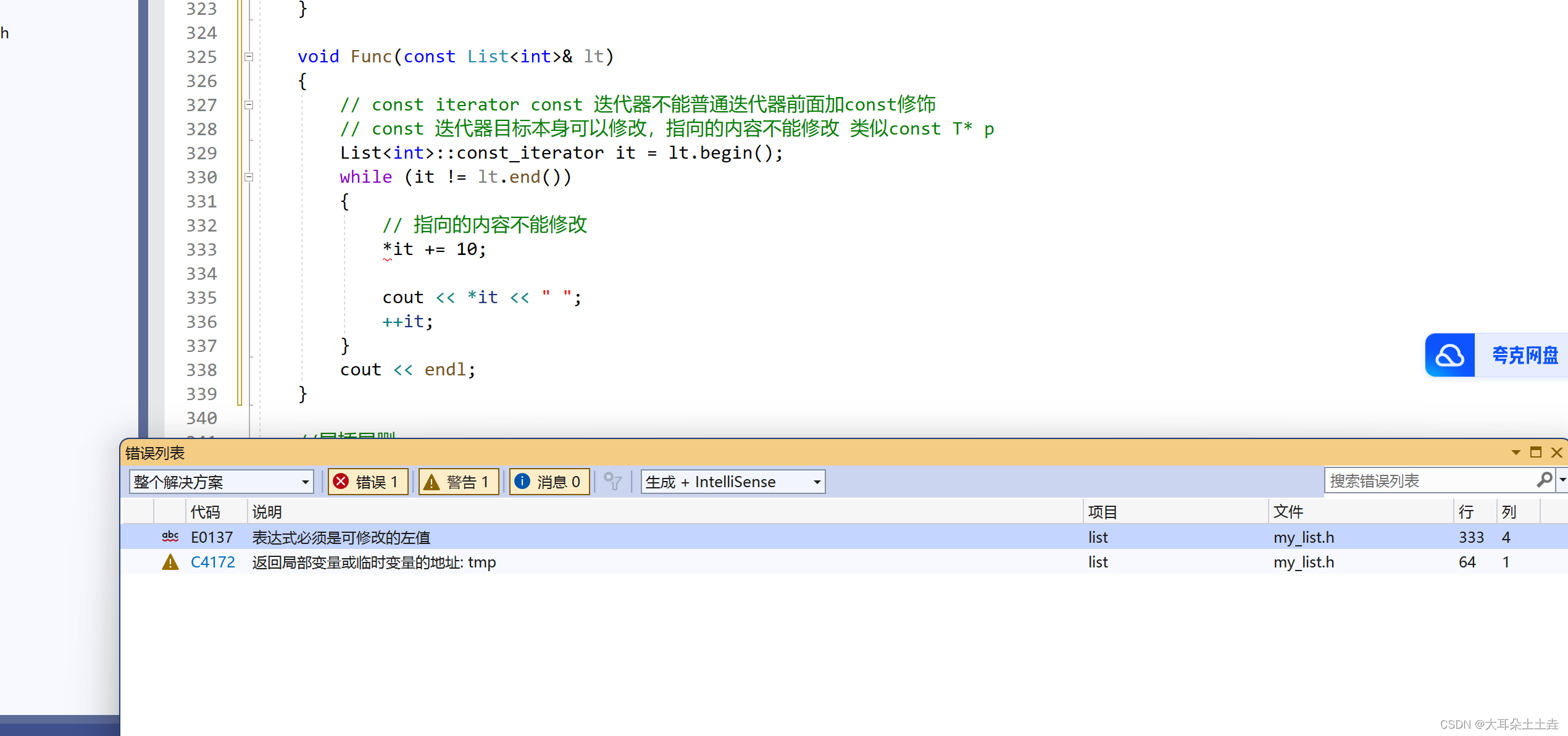
#pragma once using namespace std; #include #include namespace tutu { //1.list节点 template struct ListNode { //默认构造 struct ListNode(const T& val = T()) :_node(val) ,_prev(NULL) ,_next(NULL) { } //成员函数 T _node; ListNode* _prev; ListNode* _next; }; //2.迭代器类 template struct List_Iterator { typedef struct ListNode Node; typedef List_Iterator self; Node* _pnode; //构造函数 List_Iterator(Node* node) :_pnode(node) { } Ref operator*()const { return _pnode->_node; } Ptr operator->() const { return &_pnode->_node; } //前置++ self& operator++() { _pnode = _pnode->_next; return *this; } //后置++ self& operator++(int) { self tmp(*this); _pnode = _pnode->_next; return tmp; } //前置-- self& operator--() { _pnode = _pnode->_prev; return *this; } //后置-- self& operator--(int) { self tmp(*this); _pnode = _pnode->_prev; return tmp; } bool operator!=(const self& pnode) { return !(_pnode == pnode._pnode); } bool operator==(const self& pnode) { return _pnode == pnode._pnode; } }; const迭代器 //template //struct Const_List_Iterator //{ // typedef struct ListNode Node; // typedef Const_List_Iterator self; // Node* _pnode; // //构造函数 // Const_List_Iterator(Node* node) // :_pnode(node) // { // } // const T& operator*()const // { // return _pnode->_node; // } // const T* operator->()const // { // return &_pnode->node; // } // //前置++ // self& operator++() // { // _pnode = _pnode->_next; // return *this; // } // //后置++ // self& operator++(int) // { // self tmp(*this); // _pnode = _pnode->_next; // return tmp; // } // //前置-- // self& operator--() // { // _pnode = _pnode->_prev; // return *this; // } // //后置-- // self& operator--(int) // { // self tmp(*this); // _pnode = _pnode->_prev; // return tmp; // } // bool operator!=(const self& pnode)const // { // return !(_pnode == pnode._pnode); // } // bool operator==(const self& pnode)const // { // return _pnode == pnode._pnode; // } //}; //3.list类 template class List { public: typedef struct ListNode Node; typedef struct ListNode* pNode; //迭代器 typedef List_Iterator iterator; //const 迭代器,数据不可被修改,但可++,判断是否相等 typedef List_Iterator const_iterator; iterator begin() { return iterator(_listhead->_next); } iterator end() { return iterator(_listhead); } const_iterator begin()const { return const_iterator(_listhead->_next); } const_iterator end() const { return const_iterator(_listhead); } void EmptyInit() { _listhead = new Node(); _listhead->_prev = _listhead; _listhead->_next = _listhead; } //默认构造 List() { EmptyInit(); } //拷贝构造 List(List& lt) { EmptyInit(); for (auto& e : lt) { push_back(e); } } //initializer_list List(initializer_list il) { EmptyInit(); for (const auto& e : il) { push_back(e); } } //赋值运算符重载 List& operator=(List lt) { swap(_listhead,lt._listhead); return *this; } //清空数据 void clear() { pNode cur = _listhead->_next; pNode del = _listhead->_next; while (cur != _listhead) { cur = cur->_next; delete del; del = cur; } _listhead->_next = _listhead; _listhead->_prev = _listhead; } //析构函数 ~List() { clear(); //释放哨兵位头节点 delete _listhead; } //尾插 void push_back(const T& val = T()) { /*pNode newnode = new Node(val); newnode->_prev = _listhead->_prev; _listhead->_prev->_next = newnode; newnode->_next = _listhead; _listhead->_prev = newnode;*/ insert(end(), val); } //尾删 void pop_back() { /*if (_listhead->_prev != _listhead) { pNode tail = _listhead->_prev->_prev; delete _listhead->_prev; _listhead->_prev = tail; tail->_next = _listhead; }*/ erase(--end()); } //头插 void push_front(const T& val = T()) { /*pNode newnode = new Node(val); _listhead->_next->_prev = newnode; newnode->_next = _listhead->_next; newnode->_prev = _listhead; _listhead->_next = newnode;*/ insert(begin(), val); } //头删 void pop_front() { /*if (_listhead->_prev != _listhead) { pNode head = _listhead->_next->_next; delete _listhead->_next; _listhead->_next = head; head->_prev = _listhead; }*/ erase(begin()); } //任意位置前插入 iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x) { pNode newnode = new Node(x); pNode cur = pos._pnode; cur->_prev->_next = newnode; newnode->_prev = cur->_prev; newnode->_next = cur; cur->_prev = newnode; //返回新插入位置的迭代器 return iterator(newnode); } //任意位置删除 iterator erase(iterator pos) { assert(pos != end()); Node* cur = pos._pnode; Node* prev = cur->_prev; Node* next = cur->_next; prev->_next = next; next->_prev = prev; delete cur; return iterator(next); } private: pNode _listhead; }; //迭代器测试 void test2() { List lt1; lt1.push_back(1); lt1.push_back(2); List::iterator it = lt1.begin(); while (it != lt1.end()) { cout // const iterator const 迭代器不能普通迭代器前面加const修饰 // const 迭代器目标本身可以修改,指向的内容不能修改 类似const T* p List // 指向的内容不能修改 //*it += 10; cout List cout List cout List cout Pos(int a = 100, int b = 100) :x(a) , y(b) { } int x; int y; }; void test() { List cout //默认构造 List cout cout 1,2,3,4 ,5}; it = lt3.begin(); while (it != lt3.end()) { cout //默认构造 List cout cout //默认构造 struct ListNode(const T& val = T()) :_node(val) ,_prev(NULL) ,_next(NULL) { } //成员函数 T _node; ListNode public: typedef struct ListNode pNode newnode = new Node(val);//开辟新节点,并用val初始化 newnode-_prev = _listhead-_prev; _listhead-_prev-_next = newnode; newnode-_next = _listhead; _listhead-_prev = newnode; } if (_listhead-_prev != _listhead)//如果有节点 { pNode tail = _listhead-_prev-_prev; delete _listhead-_prev; _listhead-_prev = tail; tail-_next = _listhead; } } typedef struct ListNode } T& operator*()const { return _pnode-_node; } T* operator-() const { return &_pnode-_node; } //前置++ self& operator++() { _pnode = _pnode-_next; return *this; } //后置++ self& operator++(int)//提供一个参数区分 { self tmp(*this); _pnode = _pnode-_next; return tmp; } //前置-- self& operator--() { _pnode = _pnode-_prev; return *this; } //后置-- self& operator--(int) { self tmp(*this); _pnode = _pnode-_prev; return tmp; } bool operator!=(const self& pnode) { return !(_pnode == pnode._pnode); } bool operator==(const self& pnode) { return _pnode == pnode._pnode; } }; Pos(int a = 100, int b = 100) :x(a) , y(b) { } int x; int y; }; List cout public: typedef struct ListNode return iterator(_listhead-_next); } iterator end() { return iterator(_listhead); } private: pNode _listhead; }; List cout typedef struct ListNode } const T& operator*()const { return _pnode-_node; } const T* operator-()const { return &_pnode-node; } //前置++ self& operator++() { _pnode = _pnode-_next; return *this; } //后置++ self& operator++(int) { self tmp(*this); _pnode = _pnode-_next; return tmp; } //前置-- self& operator--() { _pnode = _pnode-_prev; return *this; } //后置-- self& operator--(int) { self tmp(*this); _pnode = _pnode->_prev; return tmp; } bool operator!=(const self& pnode)const { return !(_pnode == pnode._pnode); } bool operator==(const self& pnode)const { return _pnode == pnode._pnode; } };如下图所示const迭代器的数据不能被修改:
我们发现能够修改数据的只有这两个函数:
const T& operator*()const { return _pnode->_node; } const T* operator->()const { return &_pnode->node; }所以我们在返回值前面+const修饰其不能被修改即可,因为是const对象使用,所以后面也要+const修饰this
我们发现普通对象的迭代器和const对象使用的迭代器差异非常小,很多代码都是重复的,所以我们可以考虑使用模板来简化代码,代码如下:
template struct List_Iterator { typedef struct ListNode Node; typedef List_Iterator self; Node* _pnode; //构造函数 List_Iterator(Node* node) :_pnode(node) { } Ref operator*()const { return _pnode->_node; } Ptr operator->() const { return &_pnode->_node; } //前置++ self& operator++() { _pnode = _pnode->_next; return *this; } //后置++ self& operator++(int) { self tmp(*this); _pnode = _pnode->_next; return tmp; } //前置-- self& operator--() { _pnode = _pnode->_prev; return *this; } //后置-- self& operator--(int) { self tmp(*this); _pnode = _pnode->_prev; return tmp; } bool operator!=(const self& pnode) { return !(_pnode == pnode._pnode); } bool operator==(const self& pnode) { return _pnode == pnode._pnode; } };因为仅仅有两个函数返回值不一样,所以我们考虑多传两个模板参数,以减少代码的数量,简化代码
template class List { public: typedef struct ListNode Node; typedef struct ListNode* pNode; //迭代器 typedef List_Iterator iterator; //const 迭代器,数据不可被修改,但可++,判断是否相等 typedef List_Iterator const_iterator; iterator begin() { return iterator(_listhead->_next); } iterator end() { return iterator(_listhead); } const_iterator begin()const { return const_iterator(_listhead->_next); } const_iterator end() const { return const_iterator(_listhead); } private: pNode _listhead; };2.5头插头删
//头插 void push_front(const T& val = T()) { pNode newnode = new Node(val); _listhead->_next->_prev = newnode; newnode->_next = _listhead->_next; newnode->_prev = _listhead; _listhead->_next = newnode; }//头删 void pop_front() { if (_listhead->_prev != _listhead) { pNode head = _listhead->_next->_next; delete _listhead->_next; _listhead->_next = head; head->_prev = _listhead; } }✨头插头删测试代码
//头插头删 void test4() { List lt1; lt1.push_front(1); lt1.push_front(2); lt1.push_front(3); lt1.push_front(4); lt1.pop_front(); lt1.pop_front(); lt1.pop_front(); List::iterator it = lt1.begin(); while (it != lt1.end()) { cout pNode newnode = new Node(x);//创建新节点,并初始化 pNode cur = pos._pnode; cur-_prev-_next = newnode; newnode->_prev = cur->_prev; newnode->_next = cur; cur->_prev = newnode; //返回新插入位置的迭代器 return iterator(newnode); }有了任意位置插入,就可以在头插和尾插这里实现代码复用:
//头插 void push_front(const T& val = T()) { insert(begin(), val); } //尾插 void push_back(const T& val = T()) { insert(end(), val); }2.7任意位置删除
//任意位置删除 iterator erase(iterator pos) { assert(pos != end()); Node* cur = pos._pnode; Node* prev = cur->_prev; Node* next = cur->_next; prev->_next = next; next->_prev = prev; delete cur; return iterator(next); }注意删除任意位置之后,迭代器会失效,所以可以返回新的迭代器,然后使用时重新赋值,这样才行
有了任意位置删除,就可以在头删和尾删这里实现代码复用:
//尾删 void pop_back() { erase(--end()); } ```cpp //头删 void pop_front() { erase(begin()); }✨任意位置插入删除测试代码
//任意位置插入删除 void test5() { List lt1; List::iterator it = lt1.begin(); lt1.insert(it, 1); lt1.insert(it, 2); lt1.insert(it,3); it = lt1.begin(); it = lt1.erase(it);//更新迭代器 while (it != lt1.end()) { cout pNode cur = _listhead-_next; pNode del = _listhead-_next; while (cur != _listhead) { cur = cur->_next; delete del; del = cur; } _listhead->_next = _listhead; _listhead->_prev = _listhead; }2.9析构函数
直接复用clear函数再释放哨兵位头节点即可
//析构函数 ~List() { clear(); //释放哨兵位头节点 delete _listhead; }2.10构造函数
无论是哪个构造函数,我们都需要一个哨兵位头节点,所以可以单独写一个函数,用来复用
//哨兵位头节点 void EmptyInit() { _listhead = new Node(); _listhead->_prev = _listhead; _listhead->_next = _listhead; }✨默认构造
只需一个哨兵位头节点即可
//默认构造 List() { EmptyInit(); }✨拷贝构造
//拷贝构造 List(List& lt) { EmptyInit();/哨兵位 for (auto& e : lt) { push_back(e); } }有了哨兵位节点之后就可以遍历lt尾插实现深拷贝了
✨initializer_list构造
和拷贝构造一样,先需要一个哨兵位头节点然后遍历initializer_list,尾插实现构造
//initializer_list List(initializer_list il) { EmptyInit(); for (const auto& e : il) { push_back(e); } }✨测试代码
//构造函数测试代码 void test6() { //默认构造 List lt1; lt1.push_back(1); lt1.push_back(2); lt1.push_back(3); lt1.push_back(4); List::iterator it = lt1.begin(); while (it != lt1.end()) { cout cout 1,2,3,4 ,5}; it = lt3.begin(); while (it != lt3.end()) { cout swap(_listhead,lt._listhead); return *this; } //默认构造 List cout cout
免责声明:我们致力于保护作者版权,注重分享,被刊用文章因无法核实真实出处,未能及时与作者取得联系,或有版权异议的,请联系管理员,我们会立即处理!
部分文章是来自自研大数据AI进行生成,内容摘自(百度百科,百度知道,头条百科,中国民法典,刑法,牛津词典,新华词典,汉语词典,国家院校,科普平台)等数据,内容仅供学习参考,不准确地方联系删除处理!
图片声明:本站部分配图来自人工智能系统AI生成,觅知网授权图片,PxHere摄影无版权图库和百度,360,搜狗等多加搜索引擎自动关键词搜索配图,如有侵权的图片,请第一时间联系我们,邮箱:ciyunidc@ciyunshuju.com。本站只作为美观性配图使用,无任何非法侵犯第三方意图,一切解释权归图片著作权方,本站不承担任何责任。如有恶意碰瓷者,必当奉陪到底严惩不贷!