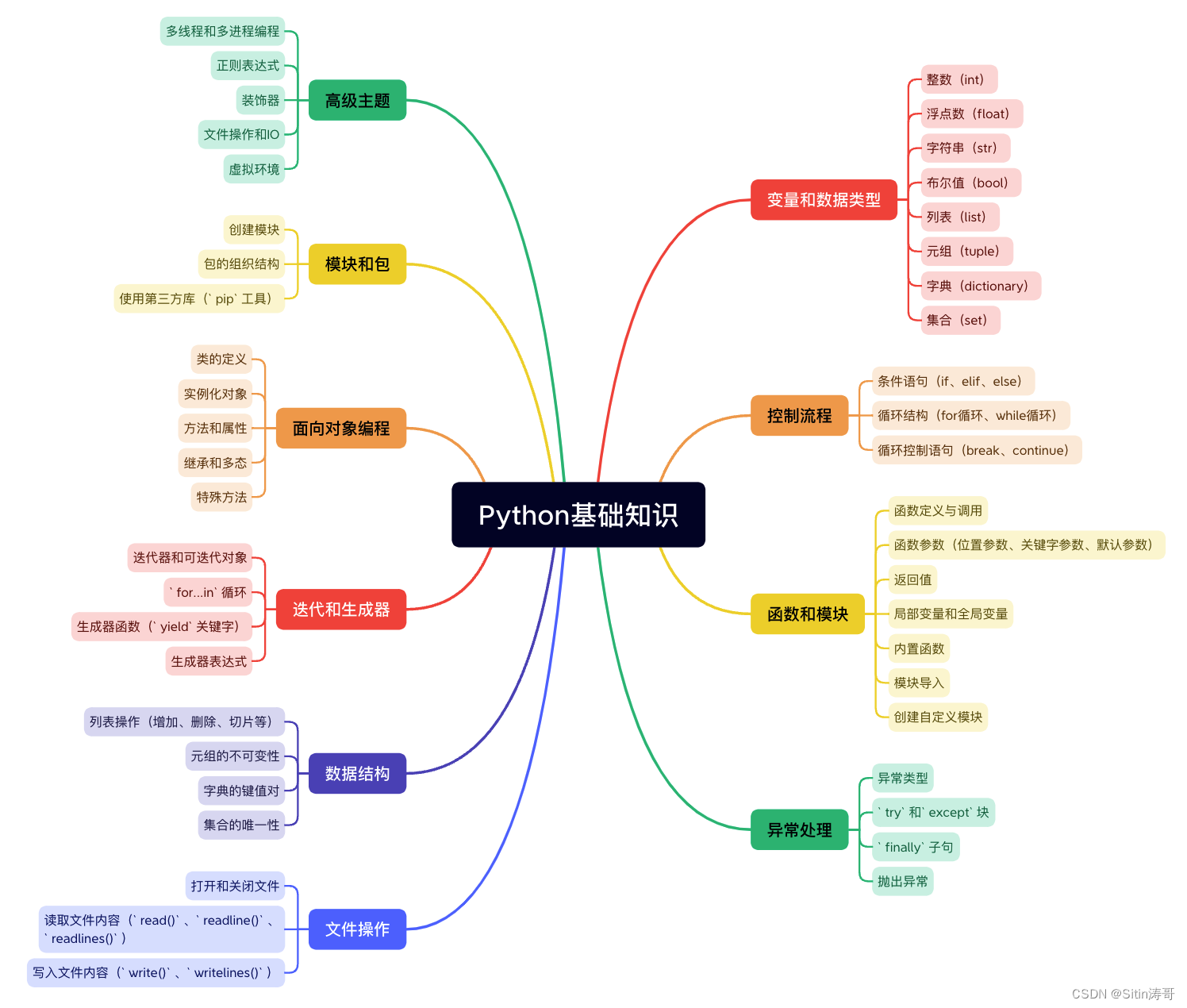
如何利用Python进行文本数据分析:深入解析与实例代码
更多资料获取
📚 个人网站:ipengtao.com
文本数据分析在当今信息时代具有重要地位,而Python作为一门强大的编程语言,提供了丰富的工具和库来处理和分析文本数据。本文将深入研究如何使用Python进行文本数据分析,提供详细全面的内容和丰富的示例代码。
读取文本数据
使用Python内置的open()函数或第三方库如pandas读取文本文件:
# 使用open()函数读取文本文件
with open('text_data.txt', 'r') as file:
text_content = file.read()
# 使用pandas读取文本文件
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('text_data.csv', delimiter='\t')
文本预处理
清理文本数据是文本分析的第一步,包括去除停用词、标点符号,转换为小写等:
import re
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
def preprocess_text(text):
text = text.lower()
text = re.sub(r'\W', ' ', text)
text = re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', text)
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('english'))
tokens = [word for word in text.split() if word not in stop_words]
return ' '.join(tokens)
preprocessed_text = preprocess_text(text_content)
词频统计
使用nltk或Counter库进行词频统计:
from nltk import FreqDist from collections import Counter # 使用nltk进行词频统计 freq_dist = FreqDist(preprocessed_text.split()) print(freq_dist.most_common(10)) # 使用Counter进行词频统计 word_count = Counter(preprocessed_text.split()) print(word_count.most_common(10))
文本情感分析
使用nltk或TextBlob库进行情感分析:
from nltk.sentiment import SentimentIntensityAnalyzer from textblob import TextBlob # 使用nltk进行情感分析 sia = SentimentIntensityAnalyzer() sentiment_nltk = sia.polarity_scores(text_content) print(sentiment_nltk) # 使用TextBlob进行情感分析 blob = TextBlob(text_content) sentiment_textblob = blob.sentiment print(sentiment_textblob)
文本相似度计算
使用nltk或gensim库进行文本相似度计算:
from nltk.metrics import jaccard_distance
from gensim.models import Word2Vec
# 使用nltk计算Jaccard相似度
text1 = "This is a sample text."
text2 = "This is another example text."
set1 = set(text1.split())
set2 = set(text2.split())
similarity_nltk = 1 - jaccard_distance(set1, set2)
print(similarity_nltk)
# 使用gensim计算Word2Vec相似度
model = Word2Vec([text1.split(), text2.split()], min_count=1)
similarity_gensim = model.wv.similarity('sample', 'example')
print(similarity_gensim)
文本分类
使用scikit-learn库进行文本分类:
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report
# 使用TfidfVectorizer将文本转换为TF-IDF特征
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer()
X = vectorizer.fit_transform(text_data)
y = labels
# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 使用Multinomial Naive Bayes进行文本分类
classifier = MultinomialNB()
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 进行预测和评估
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
print("Classification Report:\n", classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
主题建模
使用gensim库进行主题建模,例如使用Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA):
from gensim import corpora, models
# 创建语料库和字典
corpus = [text.split() for text in text_data]
dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(corpus)
# 将文本转换为词袋表示
bow_corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(text) for text in corpus]
# 使用LDA进行主题建模
lda_model = models.LdaModel(bow_corpus, num_topics=3, id2word=dictionary, passes=10)
# 打印主题
for idx, topic in lda_model.print_topics(-1):
print(f"Topic {idx + 1}: {topic}")
文本生成
使用循环神经网络 (RNN) 进行文本生成,例如使用tensorflow和keras:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Embedding, LSTM, Dense
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
# 使用Tokenizer将文本转换为序列
tokenizer = Tokenizer()
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(text_data)
total_words = len(tokenizer.word_index) + 1
# 创建输入序列
input_sequences = []
for line in text_data:
token_list = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences([line])[0]
for i in range(1, len(token_list)):
n_gram_sequence = token_list[:i+1]
input_sequences.append(n_gram_sequence)
# 对输入序列进行填充
max_sequence_length = max([len(x) for x in input_sequences])
input_sequences = pad_sequences(input_sequences, maxlen=max_sequence_length, padding='pre')
# 创建模型
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(total_words, 100, input_length=max_sequence_length-1))
model.add(LSTM(100))
model.add(Dense(total_words, activation='softmax'))
# 编译模型
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
文本可视化
使用wordcloud库制作词云图,展示词语的频率:
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 生成词云图
wordcloud = WordCloud(width=800, height=400, random_state=21, max_font_size=110).generate_from_frequencies(word_count)
# 绘制词云图
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 7))
plt.imshow(wordcloud, interpolation="bilinear")
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
自定义文本分析任务
在文本数据分析中,有时候需要执行一些定制化的任务,如命名实体识别 (NER)、关键词提取等。以下是使用两个流行的库,spaCy 和 bert-for-tf2,来执行这些任务的简单示例:
1. 命名实体识别 (NER) 使用 spaCy
import spacy
# 加载spaCy的英文模型
nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm")
# 示例文本
text = "Apple Inc. was founded by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne."
# 处理文本并进行命名实体识别
doc = nlp(text)
# 打印识别到的命名实体及其类型
for ent in doc.ents:
print(f"Entity: {ent.text}, Type: {ent.label_}")
2. 关键词提取使用 bert-for-tf2
首先,确保已经安装了 bert-for-tf2 库:
pip install bert-for-tf2
然后,执行以下示例代码:
from bert import BertModelLayer
from bert.loader import StockBertConfig, load_stock_weights
from transformers import BertTokenizer
# 加载 BERT 模型和 tokenizer
bert_model_name = 'bert-base-uncased'
bert_ckpt_dir = 'path/to/bert/ckpt/directory'
bert_tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(bert_model_name)
bert_config = StockBertConfig.from_pretrained(bert_model_name)
bert_layer = BertModelLayer.from_params(bert_config.to_json(), name='bert')
# 示例文本
text = "Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of artificial intelligence."
# 利用 tokenizer 编码文本
input_ids = bert_tokenizer.encode(text, add_special_tokens=True)
# 打印关键词
keywords = bert_tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(input_ids)
print("Keywords:", keywords)
总结
在本文中,深入研究了如何利用Python进行文本数据分析,并提供了详细而全面的示例代码。首先介绍了文本数据的读取与预处理,包括从文件读取文本、清理文本和转换为小写。接着,讨论了文本分析的核心任务,包括词频统计、情感分析、文本相似度计算和文本分类,通过使用nltk、TextBlob、scikit-learn和gensim等库提供了丰富的示例。
还深入研究了主题建模和文本生成的任务,分别利用gensim和tensorflow库展示了如何进行这些高级的文本分析。此外,介绍了使用wordcloud库制作词云图,将文本数据的关键词可视化呈现。
最后,强调了自定义文本分析任务的重要性,例如命名实体识别 (NER) 和关键词提取,并使用流行的库如spaCy和bert-for-tf2展示了相应的示例代码。通过这些定制化任务,可以更灵活地适应不同的文本分析场景。
总的来说,本文提供了一个全面的视角,涵盖了文本数据分析的各个方面。这些示例代码旨在帮助大家更好地理解和应用Python工具来处理和分析文本数据,无论是简单的词频统计,还是复杂的主题建模和文本生成任务。
Python学习路线
更多资料获取
📚 个人网站:ipengtao.com
如果还想要领取更多更丰富的资料,可以点击文章下方名片,回复【优质资料】,即可获取 全方位学习资料包。
点击文章下方链接卡片,回复【优质资料】,可直接领取资料大礼包。