【C++】---继承
【C++】---继承
- 一、继承的概念及定义
- 1、继承的概念
- 2、定义语法格式
- 3、继承基类成员访问方式的变化
- 二、基类 和 派生类 的对象之间的赋值转换
- 1、赋值规则
- 2、切片
- (1)子类对象 赋值 给 父类对象
- (2)子类对象 赋值 给 父类指针
- (3)子类对象 赋值 给 父类引用
- 三、继承中的作用域
- 1、父类和子类都有独立的作用域
- 2、隐藏的概念
- 3、如果是成员函数的隐藏,只需要函数名相同 就构成 隐藏
- 4、继承中最好不要定义同名成员
- 四、派生类的默认成员函数
- 1、规则①
- 2、规则②
- 3、规则③
- 4、规则④
- 五、继承和友元
- 六、继承和静态成员
- 七、菱形继承
- 1、单继承
- 2、多继承
- 3、菱形继承
- 八、菱形虚拟继承
- 1、虚继承
- 2、虚继承的解决数据冗余 和 二义性的原理
- 九、继承和组合
一、继承的概念及定义
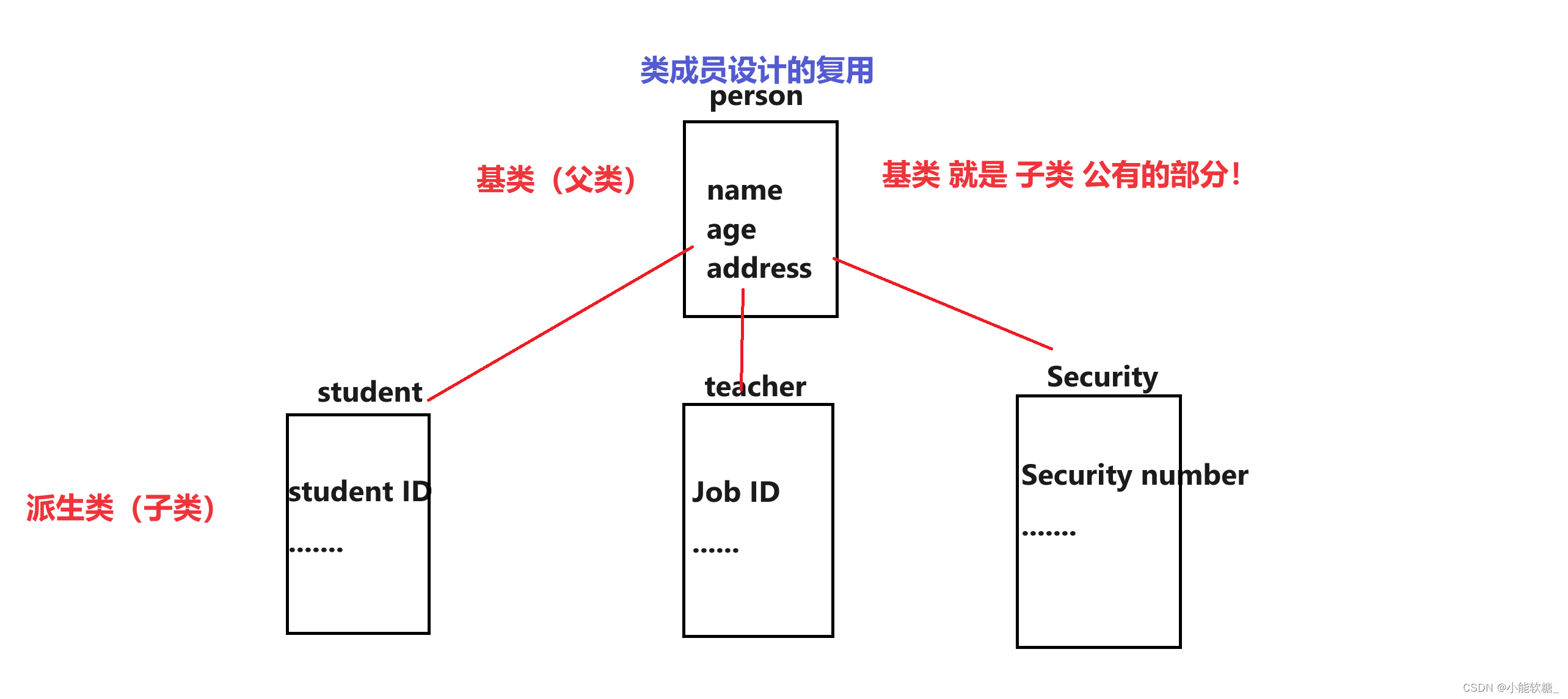
1、继承的概念
继承的概念:
继承机制是面向对象程序设计当中使代码复用的重要手段,它允许程序员,在保持原有类特性的基础上,进行拓展,增加功能,产生新的类,这个新的类就叫做:派生类。
继承的出现,呈现出面向对象程序设计的层次结构,体现了由简单到复杂的认知过程。
以前我们所接触到的复用都是函数的复用,而继承的出现则是体现了:类设计层次的复用。
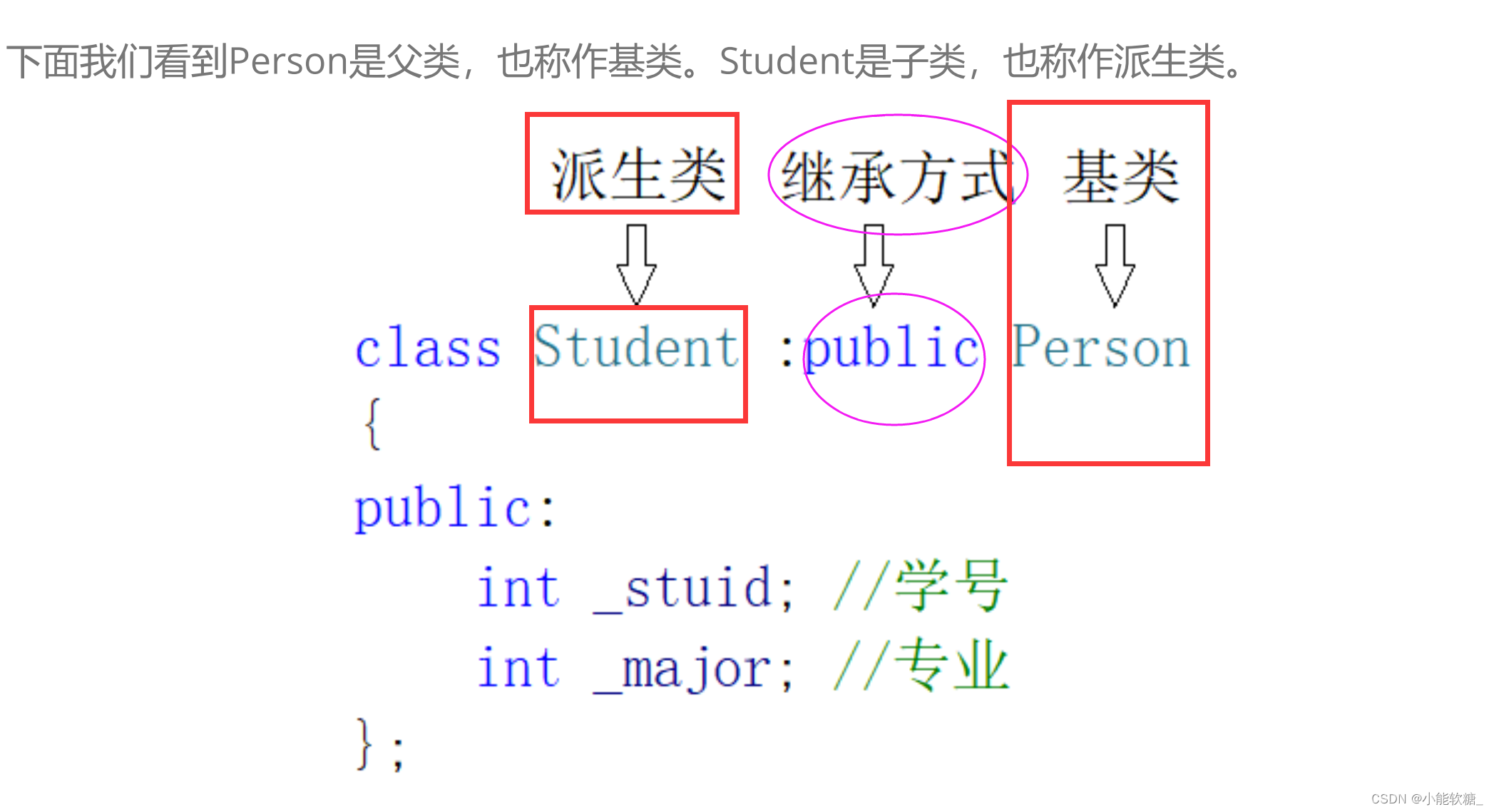
2、定义语法格式
#include using namespace std; // 基类 class Person { public: void Print() { cout protected: int stu_ID; }; // 派生类:tea class Teacher :public Person { protected: int job_ID; }; int main() { Student s; Teacher t; s.Print(); t.Print(); return 0; } public: void Print() { cout public: int stu_ID; }; int main() { Student s;// s是一个 子类对象 Person p;// p是一个 父类对象 s._name = "yjl"; s._age = 20; s.stu_ID = 20221071; p = s; s = p; return 0; } public: void Print() { cout public: int stu_ID; }; int main() { Student s;// s是一个 子类对象 //Person p;// p是一个 父类对象 Person* p;// p是一个 父类对象指针 s._name = "yjl"; s._age = 20; s.stu_ID = 20221071; p = &s; return 0; } //父类指针赋值给子类指针 Person p;//父类对象 Student *s;//子类指针 p._name = "yjl"; p._sex = "male"; p._age = 6; Person* pp = &p;//父类指针 s = (Student*)pp;//将父类指针强转为子类型指针后,再赋值给子类型指针 return 0; } //指向父类对象的父类指针,强转为子类指针后赋值给子类指针可能会造成访问越界 Person p; p._name = "yjl"; p._sex = "male"; p._age = 7; //s._No = 21530; Person* pp = &p; Student* ss = (Student*)pp; //ss-_No = 6;访问越界造成程序崩掉 return 0; } public: void Print() { cout public: int stu_ID; }; int main() { Student s;// s是一个 子类对象 //Person p;// p是一个 父类对象 //Person* p;// p是一个 父类对象指针 s._name = "yjl"; s._age = 20; s.stu_ID = 20221071; Person& p=s;// p是一个 父类对象引用 return 0; } public: string _name = "yjl"; int _age = 20; void Print1() { cout public: int _age = 100; void Print2() { cout Person p; Student s; s.Print2(); return 0; } public: string _name = "yjl"; int _age1 = 20; void Print() { cout public: int _age2 = 100; void Print(int count) { while (count) { cout Person p; Student s; // 这里的s.Print();与父类的Print 构成函数重载×××,构成函数隐藏√√√ // 父子类函数构成隐藏,只需要满足一点即可(函数名相同) s.Print();// 这里认为你用子类对象调用的是子类的打印函数,而不是你想要调用的父类打印函数。 return 0; } public: 构造 //Person(const char* name = "peter") // :_name(name) //{ // cout // cout cout cout _name = p._name; } return *this; } protected: string _name; }; // 子类 class Student :public Person { public: // 构造 Student(const char* name,int num) :Person() ,_num(num) { cout cout cout Person::operator=(s); _num = s._num; } return *this; } // 析构 ~Student() { cout Person p1; Student s1("yjl", 2022); //Student s2("yjl666", 2024); //Student s3(s1); //Person p2(s3); } int main() { test(); return 0; } cout operator=(s); _num = s._num; } return *this; } void test() { //Person p1; Student s1("yjl", 2022); Student s2("yjl666", 2024); s1 = s2;// 赋值的时候,会发生:栈溢出 //Person p2(s3); } cout Person::operator=(s); _num = s._num; } return *this; } //Person::~Person(); ~Person(); cout Person::~Person(); //~Person(); cout public: friend void Display(const Person& p, const Student& s); protected: string _name; // 姓名 }; class Student : public Person { protected: int _stuNum; // 学号 }; void Display(const Person& p, const Student& s) { cout Person p; Student s; Display(p, s); } public: Person() { _count++; } protected: string _name; public: static int _count; }; int Person::_count = 0; class Student : public Person { protected: int _ID; }; class Graduate : public Student { protected: string _course; }; void TestPerson() { Student s1; Student s2; Student s3; Graduate s4;// 在上面的继承体系中,它是单继承。 // 创建子类对象的时候必须要先构造父类对象,所以进行到此处_count等于4。 cout TestPerson(); return 0; } public: string _name; }; class Student : public Person { protected: int _num; }; class Teacher : public Person { protected: int _id; }; class Assistant :public Student, public Teacher { protected: string _course; }; void Test() { Assistant a; a._name = "peter";// 这样会有二义性无法明确知道访问的是哪一个_name // 因为,a访问的_name没有指明是student继承person的_name,还是teacher继承person的_name。 // 需要显示指定访问哪个父类的成员可以解决二义性问题,但是数据冗余问题无法解决 a.Student::_name = "xxx"; a.Teacher::_name = "xxx"; } public: string _name; }; class Student : virtual public Person { protected: int _num; }; class Teacher : virtual public Person { protected: int _id; }; class Assistant :public Student, public Teacher { protected: string _course; }; void Test() { Assistant a; a._name = "peter"; /*a.Student::_name = "xxx"; a.Teacher::_name = "xxx";*/ } int main() { Test(); return 0; } public: int _a; }; // class B : public A class B : virtual public A { public: int _b; }; // class C : public A class C : virtual public A { public: int _c; }; class D : public B, public C { public: int _d; }; int main() { D d; d.B::_a = 1; d.C::_a = 2; d._b = 3; d._c = 4; d._d = 5; return 0; } protected: string _colour = "白色"; // 颜色 string _num = "陕ABIT00"; // 车牌号 }; class BMW : public Car{ public: void Drive() {cout public: void Drive() {cout protected: string _brand = "Michelin"; // 品牌 size_t _size = 17; // 尺寸 }; class Car{ protected: string _colour = "白色"; // 颜色 string _num = "陕ABIT00"; // 车牌号 Tire _t; // 轮胎 };
免责声明:我们致力于保护作者版权,注重分享,被刊用文章因无法核实真实出处,未能及时与作者取得联系,或有版权异议的,请联系管理员,我们会立即处理!
部分文章是来自自研大数据AI进行生成,内容摘自(百度百科,百度知道,头条百科,中国民法典,刑法,牛津词典,新华词典,汉语词典,国家院校,科普平台)等数据,内容仅供学习参考,不准确地方联系删除处理!
图片声明:本站部分配图来自人工智能系统AI生成,觅知网授权图片,PxHere摄影无版权图库和百度,360,搜狗等多加搜索引擎自动关键词搜索配图,如有侵权的图片,请第一时间联系我们,邮箱:ciyunidc@ciyunshuju.com。本站只作为美观性配图使用,无任何非法侵犯第三方意图,一切解释权归图片著作权方,本站不承担任何责任。如有恶意碰瓷者,必当奉陪到底严惩不贷!