Spring学习笔记(六)利用Spring的jdbc实现学生管理系统的用户登录功能
一、案例分析
本案例要求学生在控制台输入用户名密码,如果用户账号密码正确则显示用户所属班级,如果登录失败则显示登录失败。
(1)为了存储学生信息,需要创建一个数据库。
(2)为了程序连接数据库并完成对数据的增删改查操作,需要在XML配置文件中配置数据库连接和事务等信息。
(3)在Dao层实现查询用户信息的方法。
(4)在Controller层处理业务逻辑,如判断用户输入的用户名与密码是否正确 。
二、实现步骤
首先利用idea创建Maven项目,在pom.xml中进行如下配置
4.0.0
org.example
Springjdbc
1.0-SNAPSHOT
8
8
mysql
mysql-connector-java
8.0.27
org.springframework
spring-context
5.3.26
org.springframework
spring-jdbc
5.3.26
org.springframework
spring-tx
5.3.26
org.springframework
spring-aspects
6.0.9
注意配置完后要重新构建Maven项目
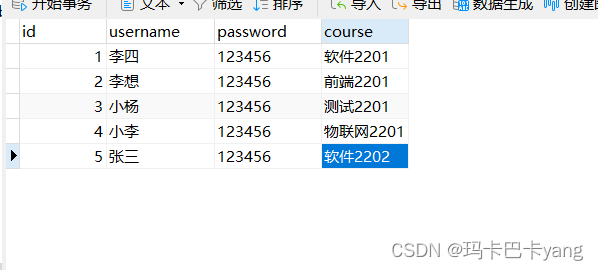
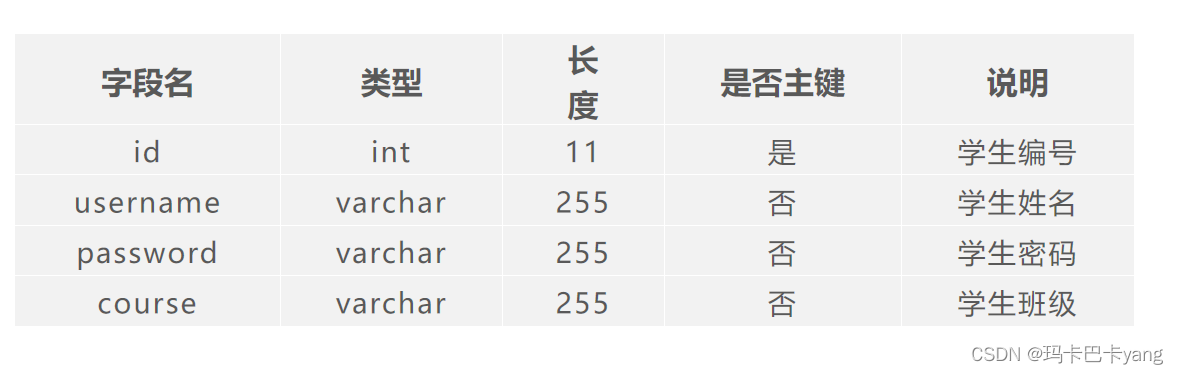
1、在数据库中创建数据表student
2、编写实体类
创建Student类,在该类中定义id、username、password和course属性,以及属性对应的getter/setter方法
package org.example.entity;
//编写实体类
public class Student {
//定义学生id
private Integer id;
//定义学生姓名
private String username;
//定义学生密码
private String password;
//定义学生课程
private String course;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getCourse() {
return course;
}
public void setCourse(String course) {
this.course = course;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", course='" + course + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
3、编写配置文件:
创建配置文件applicationContext-student.xml,在该文件中配置id为dataSource的数据源Bean和id为jdbcTemplate的JDBC模板Bean,并将数据源注入到JDBC模板中
4、编写Dao层方法:
创建StudentDao接口,在StudentDao接口中声明查询所有用户信息的方法。
package org.example.dao;
import org.example.entity.Student;
//dao层开发关联数据库,创建接口,定义方法findStudent
public interface StudentDao {
public Student findStudentByUsernameAndPassword(String username,String password);
}
5、实现Dao层方法:
创建StudentDaoImpl实现类,在StudentDaoImpl类中实现StudentDao接口中的findAllStudent()方法。
package org.example.dao.impl;
import org.example.dao.StudentDao;
import org.example.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.dao.EmptyResultDataAccessException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
//在StudentDaoImpl类中实现StudentDao接口中的findAllStudent()方法。
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao {
//实现数据库
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate() {
return jdbcTemplate;
}
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
@Override
public Student findStudentByUsernameAndPassword(String username, String password) {
// 数据库操作
String sql = "select * from student where username=? and password=?";
Student student = null;
try {
student = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper(Student.class), username, password);
} catch (EmptyResultDataAccessException e) {
// 如果没查到数据就返回空
return null;
}
return student;
}
}
6、编写Controller层:
创建StudentController类,用于实现用户登录操作。
package org.example.controller;
import org.example.dao.StudentDao;
import org.example.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.util.Scanner;
//实现业务
public class StudentController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//关联配置,实现dao层接口
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext-student.xml");
StudentDao studentDao=(StudentDao) ac.getBean("studentDao");
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("欢迎来到学生管理系统");
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
// 接收输入
String username=sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入用户密码:");
String password=sc.next();
// 逻辑查询,从数据库中查询
Student student= studentDao.findStudentByUsernameAndPassword(username,password);
if (student == null) {
// 没有查询到数据,查询的用户或密码有误
System.out.println("没有查询到数据,查询的用户或密码有误");
}else {
// 查询到数据,查询的用户或密码正确
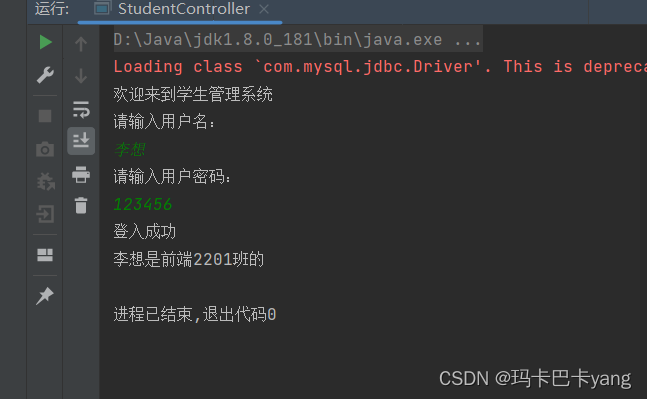
System.out.println("登入成功");
System.out.println(username+"是"+student.getCourse()+"班的");
}
}
}
7、查看运行结果:
在IDEA中启动StudentController类,在控制台按照提示输入账号密码进行登录。
三、总结spring jdbc知识
数据库用于处理持久化业务产生的数据,应用程序在运行过程中经常要操作数据库。一般情况下,数据库的操作由持久层(Dao层)来实现。作为扩展性较强的一站式开发框架,Spring也提供了持久层Spring JDBC功能,Spring JDBC可以管理数据库连接资源,简化传统JDBC的操作,进而提升程序数据库操作的效率。
1、JDBCTemplate作用
针对数据库操作,Spring框架提供了JdbcTemplate类,JdbcTemplate是一个模板类,Spring JDBC中的更高层次的抽象类均在JdbcTemplate模板类的基础上创建。 JdbcTemplate类提供了操作数据库的基本方法,包括添加、删除、查询和更新。在操作数据库时,JdbcTemplate类简化了传统JDBC中的复杂步骤,这可以让开发人员将更多精力投入到业务逻辑中。
2、Spring JDBC的配置
Spring对数据库的操作都封装在了core、dataSource、object和support这4个包中,想要使用Spring JDBC,就需要对这些包进行配置。 在Spring中,JDBC的配置是在配置文件applicationContext.xml中完成的,包括配置数据源、配置JDBC模板和配置注入类。
3、 excute()方法
在Spring JDBC中,execute()方法是JdbcTemplate类的一部分。该方法允许您执行任何SQL语句,无论是查询还是更新操作。execute()方法是一种多功能方法,可用于执行任何类型的SQL操作。
基本语法格式:jdTemplate.execute("SQL 语句");
4、update()方法
update()方法是JdbcTemplate类的一个重要方法,用于执行SQL语句来更新数据库中的数据。这个方法通常用于执行INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE等需要修改数据库记录的操作
5、query()方法
query()方法是JdbcTemplate类的一个重要方法,用于执行SELECT查询并返回一个结果集。这个方法通常用于从数据库中检索数据
6、 事务管理的核心接口
spring-tx-5.2.8.RELEAS依赖包的3个接口
PlatformTransactionManager接口:可以根据属性管理事务。
TransactionDefinition接口:用于定义事务的属性。
TransactionStatus接口:用于界定事务的状态
7、事务管理的方式
Spring中的事务管理分为两种方式,一种是传统的编程式事务管理,另一种是声明式事务管理。 编程式事务管理:通过编写代码实现的事务管理,包括定义事务的开始、正常执行后的事务提交和异常时的事务回滚。
声明式事务管理:通过AOP技术实现的事务管理,其主要思想是将事务管理作为一个“切面”代码单独编写,然后通过AOP技术将事务管理的“切面”代码植入到业务目标类中。
其中声明式事务管理有两种解决方式:基于xml的配置和基于注解的实现,如:
1.创建配置文件:创建配置文件applicationContext-annotation.xml,在该文件中声明事务管理器等配置信息。
2、修改Dao层实现类:在AccountDaoImpl类的某实现方法上添加事务注解@Transactional。
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,
isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT, readOnly = false)