【map、set】C++用红黑树来封装map、set容器

🎉博主首页: 有趣的中国人
🎉专栏首页: C++进阶
🎉其它专栏: C++初阶 | Linux | 初阶数据结构
小伙伴们大家好,本片文章将会讲解map和set之用红黑树来封装map、set容器的相关内容。
如果看到最后您觉得这篇文章写得不错,有所收获,麻烦点赞👍、收藏🌟、留下评论📝。您的支持是我最大的动力,让我们一起努力,共同成长!
文章目录
- `0. 前言`
- `1. map、set底层源码一览`
- ==⌛底层查看⏳==
- `2. 改造红黑树`
- ==⏳map类和set类⌛==
- ==⏳仿函数,这思想很重要⌛==
- ==⏳第一个K的作用⌛==
- `3. 迭代器的模拟实现`
- ==⏳迭代器++⌛==
- ==⏳迭代器- -⌛==
- `4. map的operator[]`
- `5. 拷贝构造、析构、赋值重载`
- ==⏳析构函数⌛==
- ==⏳拷贝构造⌛==
- ==⏳赋值重载⌛==
0. 前言
首先借用某位大佬的一句话:学习制造轮子不是为了打造更出色的轮子,而是为了汲取大师们卓越的思想,以此启迪我们的认知与创造力。
1. map、set底层源码一览
我们在模拟红黑树的时候一律用了pair的KV模型来进行实现。但是由于map是KV模型的而set是K型的,但是底层都是用的红黑树,那么应该如何进行调整呢?
⌛底层查看⏳
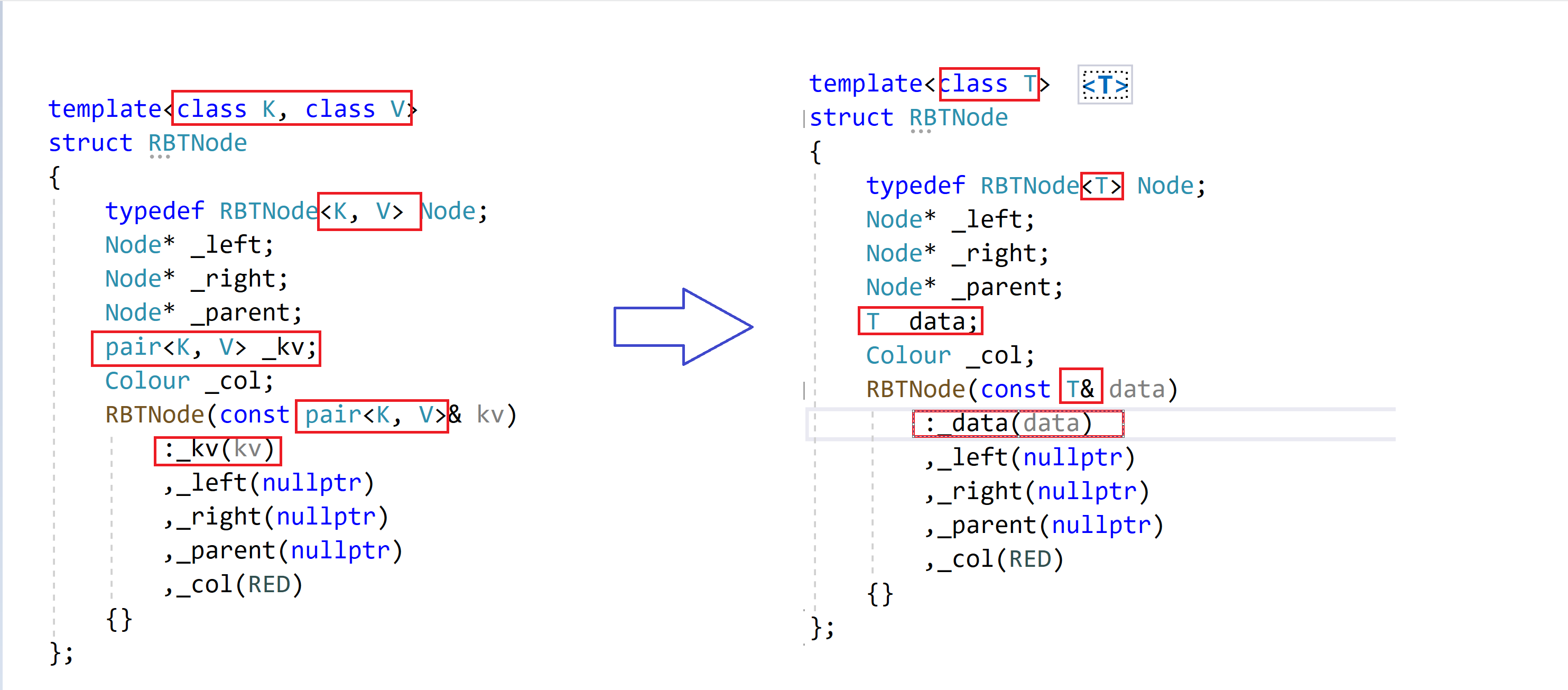
可以看到,对于K类型的set,模板传入了两个相同的K类型给RBTree;对于KV类型的map,模板传入了一个K,还有一个pair类型给RBTree。
在RBTree类中将第二个模板参数传入给RBTreeNode,data的数据类型为就是此类型,这样就解决了此问题。
2. 改造红黑树
⏳map类和set类⌛
我们先按照底层的思路实现以下map类和set类:
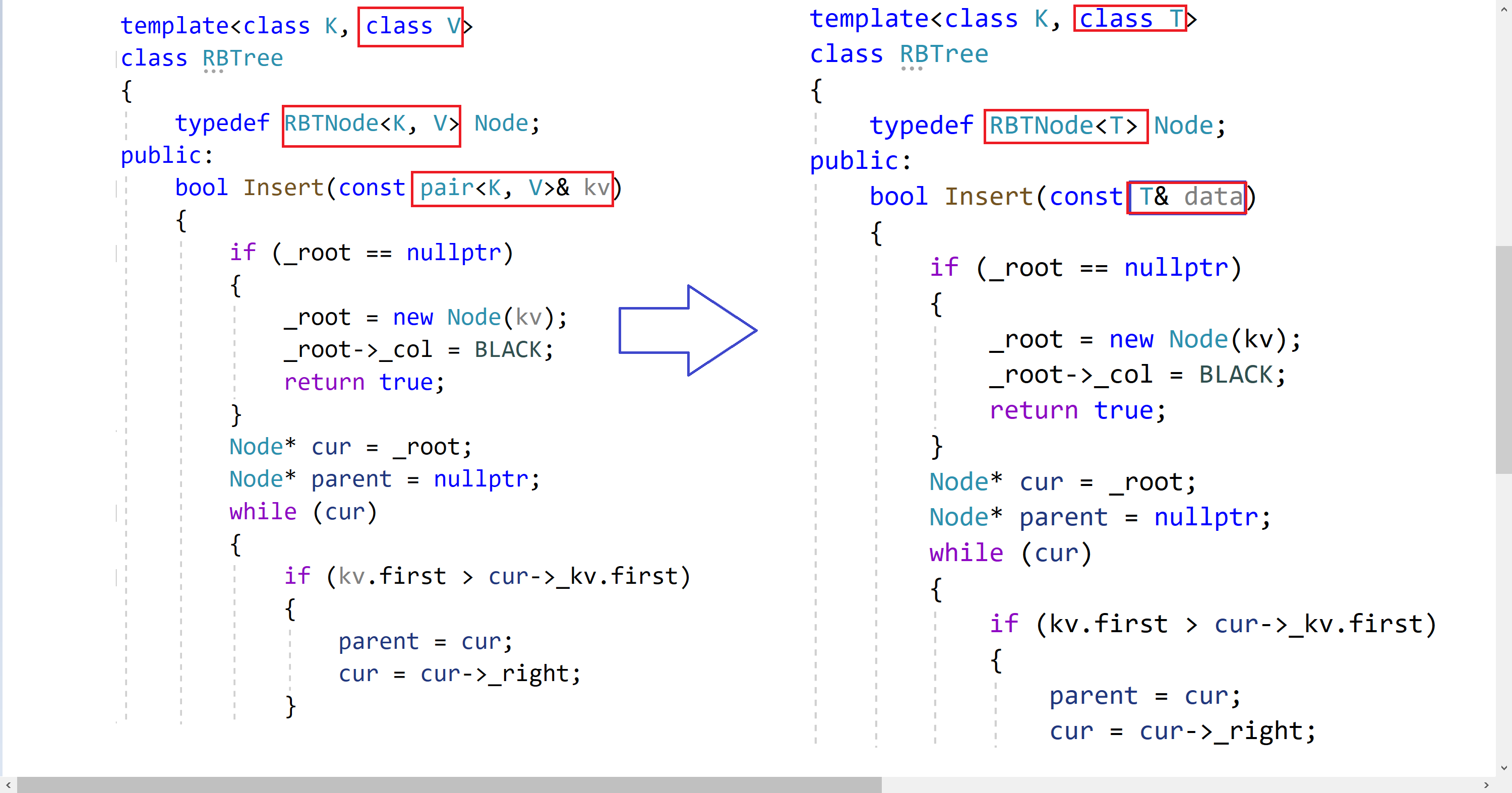
// mymap.h #pragma once #include "RBTtree.h" namespace dsj { template class map { public: private: // pair 为节点中的参数类型 RBTree rt; }; } // myset.h #pragma once #include "RBTtree.h" namespace dsj { template class set { public: private: // 第二个 K 为节点中的参数类型 RBTree rt; }; }💻RBTreeNode的修改
💻RBTree的修改
这样一改,问题就来了,在我们插入数据的时候,如何根据插入节点的K值来判断他插入所在的位置呢?如何进行比较?
可以用仿函数来进行比较。
⏳仿函数,这思想很重要⌛
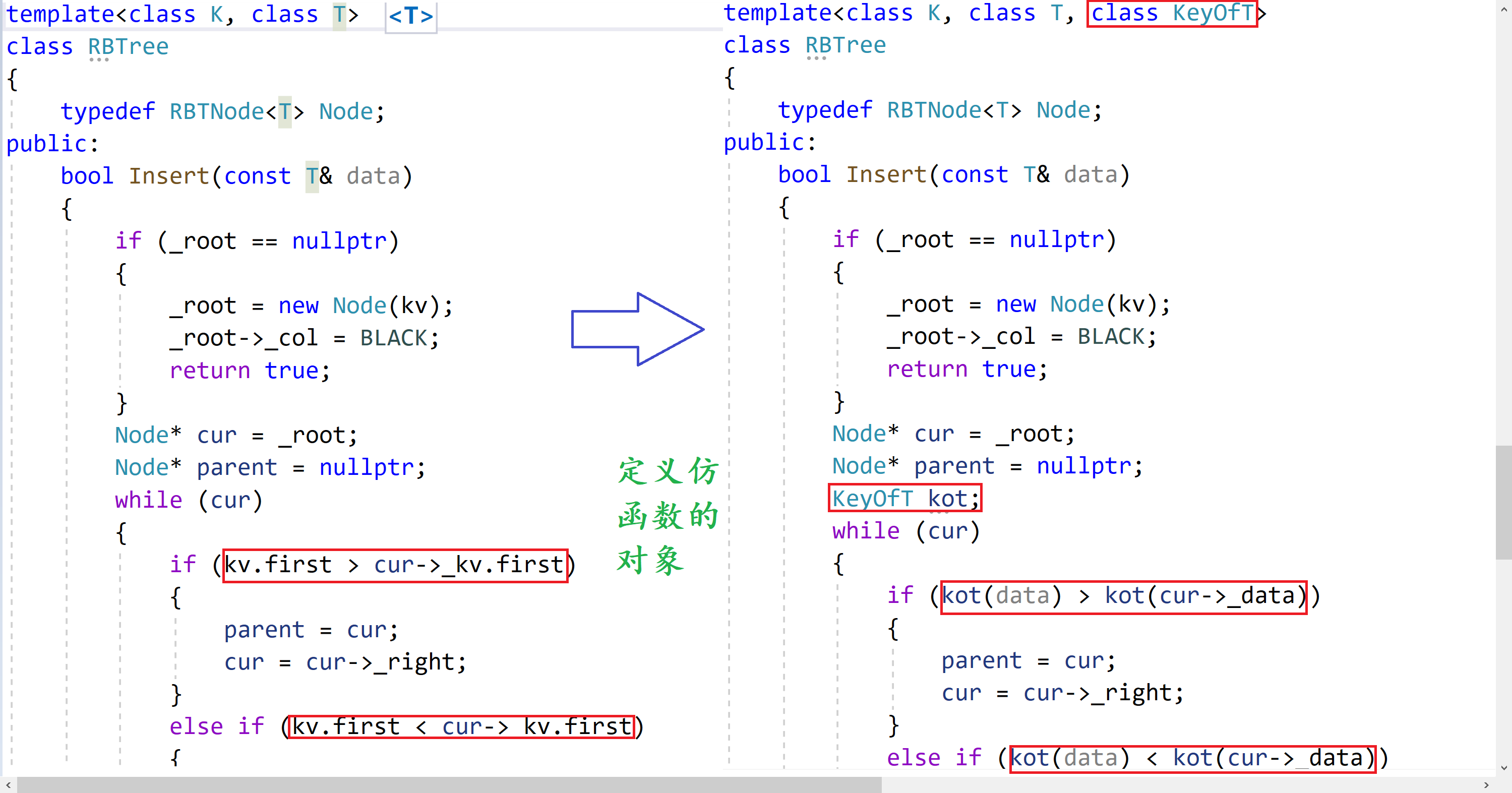
虽然在RBTree中并不知道如何进行比较,但是在map和set类中知道如何进行比较,即map用pair的first进行比较,set直接用K值进行比较,实现方法如下:
// mymap.h namespace dsj { // 仿函数 template struct mapKeyOfT { // 取pair的first const K& operator()(const pair& kv) { return kv.first; } }; template class map { public: private: // 多加一个仿函数模板参数,对于map,取pair的first进行比较 RBTree rt; }; } // myset.h namespace dsj { // 仿函数 template struct setKeyOfT { // 取出key const K& operator()(const K& key) { return key; } }; template class set { public: private: // 多加一个仿函数模板参数,对于set,直接对K值进行比较 RBTree rt; }; }⏳第一个K的作用⌛
有一个问题,给红黑树传模板参数的时候,第一个参数K类型的作用是什么呢?
1. 对于insert来说,set和map都可以不要第一个模板参数K,因为set中第二个模板参数是K,可以用来进行插入时的比较,对于map,也是用第二个模板参数来进行比较;
2. 但是对于find接口,他就需要K;
3. 迭代器的模拟实现
通过list的迭代器,我们知道如果原生指针的效果达不到我们想要的效果,就通过封装迭代器,再用运算符重载来达到我们预期的效果。
模拟实现:
template struct __RBTIterator { typedef RBTNode Node; typedef __RBTIterator Self; Node* _node; __RBTIterator(Node* node) :_node(node) {} T operator*() { return _node->_data; } T* operator->() { return &_node->_data; } bool operator!=(const Self& s) { return _node != s._node; } };我们在模拟实现list的迭代器的时候讲过,对于const迭代器和普通迭代器,他们只有解引用和->的的返回值不一样,其他都相同,如果重新写一遍那么代码肯定非常冗余,因此我们这里还用类似的方法来实现(传入模板参数)。
改造后:
template struct __RBTIterator { typedef RBTNode Node; typedef __RBTIterator Self; Node* _node; __RBTIterator(Node* node) :_node(node) {} Ref operator*() { return _node->_data; } Ptr operator->() { return &_node->_data; } bool operator!=(const Self& s) { return _node != s._node; } };RBTree中:
// 编译器自动推演,根据类型调用对应的迭代器 typedef __RBTIterator Iterator; typedef __RBTIterator Const_Iterator; Iterator begin() { Node* leftMin = _root; // 加上leftMin是为了预防_root为空的情况 if (leftMin && leftMin->_left) { leftMin = leftMin->_left; } return Iterator(leftMin); } Iterator End() { return Iterator(nullptr); } Const_Iterator begin() const { Node* leftMin = _root; if (leftMin && leftMin->_left) { leftMin = leftMin->_left; } return Const_Iterator(leftMin); } Const_Iterator End() const { return Const_Iterator(nullptr); }map和set中:
template class map { public: typedef typename RBTree::Iterator iterator; typedef typename RBTree::Const_Iterator const_iterator; const_iterator begin() const { return rt.Begin(); } const_iterator end() const { return rt.End(); } iterator begin() { return rt.Begin(); } iterator end() { return rt.End(); } private: RBTree rt; }; template class set { public: typedef typename RBTree::Iterator iterator; typedef typename RBTree::Const_Iterator const_iterator; const_iterator beign() const { return rt.Begin(); } const_iterator end() const { return rt.End(); } iterator beign() { return rt.Begin(); } iterator end() { return rt.End(); } private: RBTree rt; };调用逻辑:
⏳迭代器++⌛
set和map迭代器的++按照中序遍历的顺序进行加加的,顺序为:左子树 根 右子树。
逻辑如下:
- 右子树存在,下一个访问节点是右子树的最左节点;
- 右子树不存在,向上找,找到孩子是父亲左节点的那个祖先节点。
代码:
Self& operator++() { Node* cur = _node; if (cur->_right) { Node* rightMin = cur->_right; while (rightMin->_left) { rightMin = rightMin->_left; } _node = rightMin; } else { Node* parent = cur->_parent; // 这里加parent是为了预防访问最右节点后parent为空的情况 while (parent && cur == parent->_right) { cur = parent; parent = cur->_parent; } _node = parent; } return *this; }⏳迭代器- -⌛
思路同上,但是顺序相反:右子树 根 左子树。
逻辑如下:
- 左子树存在,下一个访问节点是左子树的最右节点;
- 左子树不存在,向上找,找到孩子是父亲右节点的那个祖先节点。
代码:
Self& operator--() { if (_node->_left) { Node* cur = _node->_left; while (cur->_right) { cur = cur->_right; } _node = cur; } else { Node* cur = _node; Node* parent = cur->_parent; while (parent && cur == parent->_left) { cur = parent; parent = cur->_parent; } _node = parent; } return *this; }4. map的operator[]
map的operator[]的用法在之前的文章中讲过,它的作用是根据key的值进行查找,如果存在,那么就返回当前节点的value,如果不存在,就先插入此节点,然后再返回这个节点的value。
实现代码:
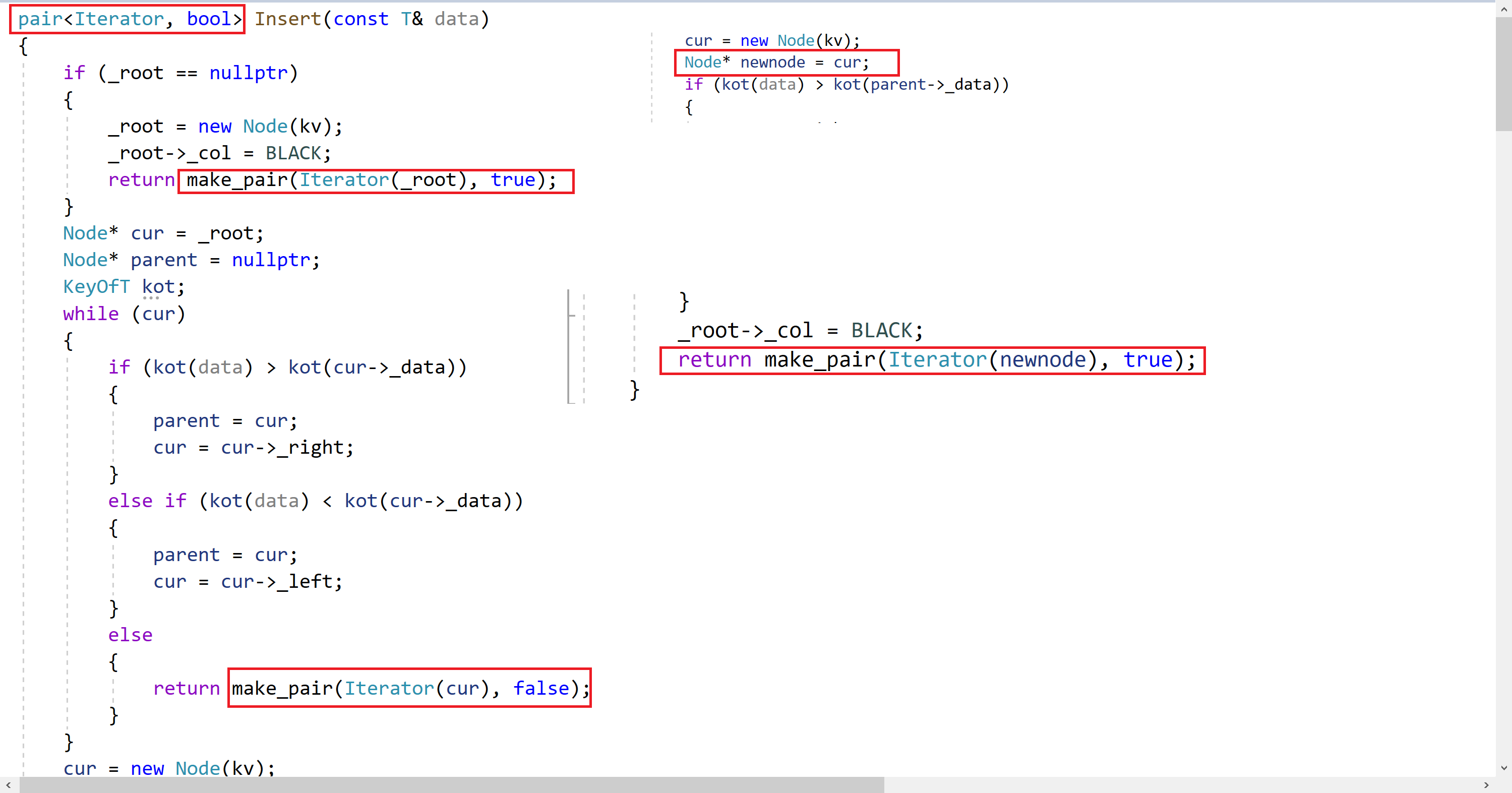
V& operator[](const K& key) { pair ret = rt.Insert(make_pair(key,V())); return ret.first->second; }Insert函数修改逻辑:
Insert函数,我们要改变它的返回值,返回值是pair:
- 如果插入成功,返回插入节点所在的迭代器;
- 如果插入失败,返回K值相等的节点的迭代器。
- 如果要进行旋转,要先记录一下当前cur的节点,因为旋转后cur的节点可能就不是我们新插入的节点了。
5. 拷贝构造、析构、赋值重载
⏳析构函数⌛
析构函数要用后序,这样更为简单:
~RBTree() { Destroy(_root); } void Destroy(Node* root) { // 左右根的顺序进行析构 if (root == nullptr) { return; } Destroy(root->_left); Destroy(root->_right); delete root; }⏳拷贝构造⌛
拷贝构造要用先序:
RBTree(const RBTree& t) { _root = Copy(t._root); } Node* Copy(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) return nullptr; Node* newroot = new Node(root->_data); newroot->_col = root->_col; newroot->_left = Copy(root->_left); if (newroot->_left) newroot->_left->_parent = newroot; newroot->_right = Copy(root->_right); if (newroot->_right) newroot->_right->_parent = newroot; return newroot; }⏳赋值重载⌛
下面是现代写法,之前讲过:
const RBTree& operator=(const RBTree t) { swap(_root, t._root); return *this; }